The complexity of phosphorylated H2AX foci formation and DNA repair assembly at DNA double-strand breaks
- PMID: 20046100
- PMCID: PMC3086803
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.9.2.10475
The complexity of phosphorylated H2AX foci formation and DNA repair assembly at DNA double-strand breaks
Abstract
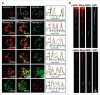
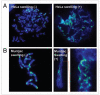
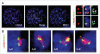
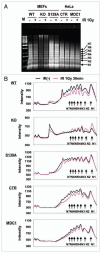
The maintenance of genome stability requires efficient DNA double-stranded break (DSB) repair mediated by the phosphorylation of multiple histone H2AX molecules near the break sites. The phosphorylated H2AX (gammaH2AX) molecules form foci covering many megabases of chromatin. The formation of gamma-H2AX foci is critical for efficient DNA damage response (DDR) and for the maintenance of genome stability, however, the mechanisms of protein organization in foci is largely unknown. To investigate the nature of gammaH2AX foci formation, we analyzed the distribution of gammaH2AX and other DDR proteins at DSB sites using a variety of techniques to visualize, expand and partially disrupt chromatin. We report here that gammaH2AX foci change composition during the cell cycle, with proteins 53BP1, NBS1 and MRE11 dissociating from foci in G(2) and mitosis to return at the beginning of the following G(1). In contrast, MDC1 remained colocalized with gamma-H2AX during mitosis. In addition, while gammaH2AX was found to span large domains flanking DSB sites, 53BP1 and NBS1 were more localized and MDC1 colocalized in doublets in foci. H2AX and MDC1 were found to be involved in chromatin relaxation after DSB formation. Our data demonstrates that the DSB repair focus is a heterogeneous and dynamic structure containing internal complexity.
Figures


Comment in
-
DNA double strand breaks: not all foci are created equal.Cell Cycle. 2010 Feb 1;9(3):442-3. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20130448 No abstract available.
-
Shifting focus.Cell Cycle. 2010 Feb 1;9(3):443-4. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20130449 No abstract available.
-
The anatomy and cell cycle evolution of DNA damage signaling and repair foci.Cell Cycle. 2010 Feb 1;9(3):444-5. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20130450 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fernandez-Capetillo O, Celeste A, Nussenzweig A. Focusing on foci: H2AX and the recruitment of DNA-damage response factors. Cell Cycle. 2003;2:426–7. - PubMed
-
- Paull TT, Rogakou EP, Yamazaki V, Kirchgessner CU, Gellert M, Bonner WM. A critical role for histone H2AX in recruitment of repair factors to nuclear foci after DNA damage. Curr Biol. 2000;10:886–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
