Liquid Chromatographic Determination of NSC 737664 (ABT-888: an Inhibitor of Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase (PARP)) in Plasma and Urine in a Phase 0 Clinical Trial
- PMID: 20046211
- PMCID: PMC2615403
- DOI: 10.1080/10826070802603351
Liquid Chromatographic Determination of NSC 737664 (ABT-888: an Inhibitor of Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase (PARP)) in Plasma and Urine in a Phase 0 Clinical Trial
Abstract
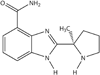
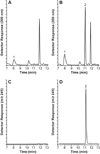
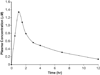
A gradient reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatographic method was developed for determining NSC 737664 (2-[(2R)-2-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]-1H-benzimidazole-4-carboxamide; ABT-888) in human plasma and urine. Chromatographic separation used a mobile phase composed of 0.1% formic acid in water and 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile, and a C18 column (150 mm × 4.6 mm, 5µ). Quantitation was performed using UV detection at 300 nm. Chromatographic peak identity was confirmed using positive-ion electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. The method was shown to be specific, accurate and reproducible, and thereby appropriate for monitoring plasma and urine levels of the agent in support of a phase 0 clinical study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometric assay for the quantitation in human plasma of ABT-888, an orally available, small molecule inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2008 Sep 1;872(1-2):141-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2008.07.032. Epub 2008 Jul 31. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18692448 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous determination of ABT-888, a poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, and its metabolite in human plasma by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2010 Feb 1;878(3-4):333-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2009.11.037. Epub 2009 Nov 27. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20005184 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Determination of chlorpropham residues in animal-derived foods by solid phase extraction and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry].Se Pu. 2022 Jan;40(1):41-47. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.02009. Se Pu. 2022. PMID: 34985214 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Simultaneous determination of 12 lipophilic shellfish toxins in plasma and urine by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry].Se Pu. 2021 Apr 8;39(4):399-405. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.11001. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34227760 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Determination of sixteen antibiotics and four β-agonists in human urine samples using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry based on high-throughput automatic solid-phase extraction].Se Pu. 2023 May 8;41(5):397-408. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2022.08025. Se Pu. 2023. PMID: 37087605 Free PMC article. Chinese.
Cited by
-
A rapid and sensitive method for determination of veliparib (ABT-888), in human plasma, bone marrow cells and supernatant by using LC/MS/MS.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2010 May 1;52(1):122-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2009.12.015. Epub 2009 Dec 29. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2010. PMID: 20071126 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Oxadiazole-Quinoxalines as Hybrid Scaffolds with Antitumor Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 8;26(4):1439. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041439. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40003907 Free PMC article.
-
Phase 0 clinical trial of the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor ABT-888 in patients with advanced malignancies.J Clin Oncol. 2009 Jun 1;27(16):2705-11. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.19.7681. Epub 2009 Apr 13. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19364967 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Increased poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation in skeletal muscle tissue of pediatric patients with severe burn injury: prevention by propranolol treatment.Shock. 2011 Jul;36(1):18-23. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e3182168d8f. Shock. 2011. PMID: 21368715 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration of poly(ADP-ribose) metabolism affects murine sperm nuclear architecture by impairing pericentric heterochromatin condensation.Chromosoma. 2013 Aug;122(4):319-35. doi: 10.1007/s00412-013-0416-y. Epub 2013 Jun 1. Chromosoma. 2013. PMID: 23729169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Curtin N. Therapeutic potential of drugs to modulate DNA repair in cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. 2007;11(6):783–799. Review. - PubMed
-
- De Murcia G, Menissier De Murcia J. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: a molecular nick-sensor. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1994;19:172–176. - PubMed
-
- Schreiber V, Dantzer F, Ame JC, De Murcia G. Poly(ADP-ribose): novel functions for an old molecule. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006;7:517–528. - PubMed
-
- Ratnam K, Low JA. Current development of clinical inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in oncology. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007;13(5):1383–1388. Review. - PubMed
-
- Plummer R, Middleton M, Wilson R, Jones C, Evans J, Robson L, Steinfeldt H, Kaufman R, Reich S, Calvert AH. First in human phase I trial of the PARP inhibitor AG-014699 with temozolomide (TMZ) in patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005;23(16S):3065.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
