Effect of sildenafil on neuropathic pain and hemodynamics in rats
- PMID: 20046518
- PMCID: PMC2799976
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.1.82
Effect of sildenafil on neuropathic pain and hemodynamics in rats
Abstract
Purpose: The inhibition of phosphodiesterase 5 produces an antinociception through the increase of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), and increasing cGMP levels enhance the release of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Furthermore, this phosphodiesterase 5 plays a pivotal role in the regulation of the vasodilatation associated to cGMP. In this work, we examined the contribution of GABA receptors to the effect of sildenafil, a phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor, in a neuropathic pain rat, and assessed the hemodynamic effect of sildenafil in normal rats.
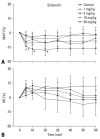
Materials and methods: Neuropathic pain was induced by ligation of L5/6 spinal nerves in Sprague-Dawley male rats. After observing the effect of intravenous sildenafil on neuropathic pain, GABAA receptor antagonist (bicuculline) and GABAB receptor antagonist (saclofen) were administered prior to delivery of sildenafil to determine the role of GABA receptors in the activity of sildenafil. For hemodynamic measurements, catheters were inserted into the tail artery. Mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR) were measured over 60 min following administration of sildenafil.
Results: Intravenous sildenafil dose-dependently increased the withdrawal threshold to the von Frey filament application in the ligated paw. Intravenous bicuculline and saclofen reversed the antinociception of sildenafil. Intravenous sildenafil increased the magnitude of MAP reduction at the maximal dosage, but it did not affect HR response.
Conclusion: These results suggest that sildenafil is active in causing neuropathic pain. Both GABAA and GABAB receptors are involved in the antinociceptive effect of sildenafil. Additionally, intravenous sildenafil reduces MAP without affecting HR.
Keywords: Antinociception; GABA receptor; Sprague-Dawley rat; hemodynamics; neuropathic pain; sildenafil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
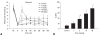

Similar articles
-
Spinal GABA(A) and GABA(B) receptor pharmacology in a rat model of neuropathic pain.Anesthesiology. 2002 May;96(5):1161-7. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200205000-00020. Anesthesiology. 2002. PMID: 11981157
-
Effects of sildenafil citrate on human hemodynamics.Am J Cardiol. 1999 Mar 4;83(5A):13C-20C. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(99)00043-0. Am J Cardiol. 1999. PMID: 10078538 Clinical Trial.
-
GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of GABAA receptor calcium elevations in developing hypothalamic neurons.J Neurophysiol. 1998 Mar;79(3):1360-70. doi: 10.1152/jn.1998.79.3.1360. J Neurophysiol. 1998. PMID: 9497417
-
Relief of hypersensitivity after nerve injury from systemic donepezil involves spinal cholinergic and γ-aminobutyric acid mechanisms.Anesthesiology. 2013 Jan;118(1):173-80. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e318277a81c. Anesthesiology. 2013. PMID: 23221863
-
GABAA but not GABAB receptors in the rostral anterior cingulate cortex selectively modulate pain-induced escape/avoidance behavior.Exp Neurol. 2007 Mar;204(1):182-94. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.10.007. Epub 2006 Dec 4. Exp Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17141761 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of phosphodiesterase 9A reduces cytokine-stimulated in vitro adhesion of neutrophils from sickle cell anemia individuals.Inflamm Res. 2011 Jul;60(7):633-42. doi: 10.1007/s00011-011-0315-8. Epub 2011 Feb 20. Inflamm Res. 2011. PMID: 21336703
-
The Role of Sildenafil in Treating Brain Injuries in Adults and Neonates.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 May 10;16:879649. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.879649. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35620219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the Antihyperalgesic Potential of Sildenafil-Metformin Combination and Its Impact on Biochemical Markers in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Neuropathy in Rats.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jun 14;17(6):783. doi: 10.3390/ph17060783. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38931450 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Multifaceted Potential of Sildenafil in Medicine.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Dec 17;59(12):2190. doi: 10.3390/medicina59122190. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 38138293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of sildenafil on the anticonvulsant action of selected antiepileptic drugs against pentylenetetrazole-induced clonic seizures in mice.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2012 Aug;119(8):923-31. doi: 10.1007/s00702-012-0767-1. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2012. PMID: 22315091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dworkin RH, O'Connor AB, Backonja M, Farrar JT, Finnerup NB, Jensen TS, et al. Pharmacologic management of neuropathic pain: evidence-based recommendations. Pain. 2007;132:237–251. - PubMed
-
- Finnerup NB, Sindrup SH, Jensen TS. Chronic neuropathic pain: mechanisms, drug targets and measurement. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2007;21:129–136. - PubMed
-
- Wallace JM. Update on pharmacotherapy guidelines for treatment of neuropathic pain. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2007;11:208–214. - PubMed
-
- Chizh BA, Göhring M, Tröster A, Quartey GK, Schmelz M, Koppert W. Effects of oral pregabalin and aprepitant on pain and central sensitization in the electrical hyperalgesia model in human volunteers. Br J Anaesth. 2007;98:246–254. - PubMed
-
- Shim B, Kim DW, Kim BH, Nam TS, Leem JW, Chung JM. Mechanical and heat sensitization of cutaneous nociceptors in rats with experimental peripheral neuropathy. Neuroscience. 2005;132:193–201. - PubMed

