Strategies for enhanced drug delivery to the central nervous system
- PMID: 20046703
- PMCID: PMC2792490
- DOI: 10.4103/0250-474X.41446
Strategies for enhanced drug delivery to the central nervous system
Abstract
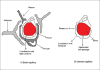
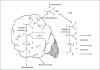
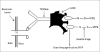
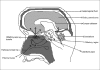
Treating central nervous system diseases is very challenging because of the presence of a variety of formidable obstacles that impede drug delivery. Physiological barriers like the blood-brain barrier and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier as well as various efflux transporter proteins make the entry of drugs into the central nervous system very difficult. The present review provides a brief account of the blood brain barrier, the P-glycoprotein efflux and various strategies for enhancing drug delivery to the central nervous system.
Keywords: CNS drug delivery; blood brain barrier; nano particles; p-glycoprotein.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transporters at CNS barrier sites: obstacles or opportunities for drug delivery?Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(10):1422-49. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990463. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 23789948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ABC efflux transporters at blood-central nervous system barriers and their implications for treating spinal cord disorders.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Jul;15(7):1235-1242. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.272568. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 31960802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of drug efflux transporters in the brain for drug disposition and treatment of brain diseases.Prog Neurobiol. 2005 May;76(1):22-76. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.04.006. Prog Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16011870 Review.
-
The barrier and interface mechanisms of the brain barrier, and brain drug delivery.Brain Res Bull. 2022 Nov;190:69-83. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.09.017. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Brain Res Bull. 2022. PMID: 36162603 Review.
-
Kinetic and biochemical analysis of carrier-mediated efflux of drugs through the blood-brain and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers: importance in the drug delivery to the brain.J Control Release. 1999 Nov 1;62(1-2):179-86. doi: 10.1016/s0168-3659(99)00036-x. J Control Release. 1999. PMID: 10518649 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting anti-HIV drugs to the CNS.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2009 Aug;6(8):771-84. doi: 10.1517/17425240903081705. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2009. PMID: 19566446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropathogenesis of HIV and emerging therapeutic targets.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2022 Jul;26(7):603-615. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2022.2100253. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2022. PMID: 35815686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moringa oleifera and Musa sapientum ameliorated 7,12-Dimethylbenz[a]anthracene-induced upregulations of Ki67 and multidrug resistance 1 genes in rats.Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2021 May-Jun;15(3):26-33. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2021. PMID: 34234633 Free PMC article.
-
Current Chemical, Biological, and Physiological Views in the Development of Successful Brain-Targeted Pharmaceutics.Neurotherapeutics. 2022 Apr;19(3):942-976. doi: 10.1007/s13311-022-01228-5. Epub 2022 Apr 7. Neurotherapeutics. 2022. PMID: 35391662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incorporation of Levodopa into Biopolymer Coatings Based on Carboxylated Carbon Nanotubes for pH-Dependent Sustained Release Drug Delivery.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018 May 31;8(6):389. doi: 10.3390/nano8060389. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29857532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martin B, Robert L, Henry B, Mathiowitz E. Encyclopedia of controlled drug delivery. Vol. 1. New York: John Wiley and Sons Inc; 1999. pp. 184–210.
-
- Pardridge WM. Recent advances in blood-brain barrier transport. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1988;28:25–39. - PubMed
-
- Tamargo RJ, Brem H. Transporting therapeutics across the blood-brain barrier. Neurosurg. 1992;2:259–79.
-
- Abbott NJ, Romero IA. Transporting therapeutics across the blood-brain barrier. Mol Med Today. 1996;3:106–13. - PubMed
-
- Gelperina SE, Khalansky AS, Skidan IN, Smirnova ZS, Bobruskin AI, Severin SE, et al. Toxicological studies of doxorubicin bound to polysorbate 80-coated poly (butyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles in healthy rats and rats with intracranial glioblastoma. Toxicol Lett. 2002;126:131–41. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
