Strategies for enhanced drug delivery to the central nervous system
- PMID: 20046703
- PMCID: PMC2792490
- DOI: 10.4103/0250-474X.41446
Strategies for enhanced drug delivery to the central nervous system
Abstract
Treating central nervous system diseases is very challenging because of the presence of a variety of formidable obstacles that impede drug delivery. Physiological barriers like the blood-brain barrier and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier as well as various efflux transporter proteins make the entry of drugs into the central nervous system very difficult. The present review provides a brief account of the blood brain barrier, the P-glycoprotein efflux and various strategies for enhancing drug delivery to the central nervous system.
Keywords: CNS drug delivery; blood brain barrier; nano particles; p-glycoprotein.
Figures
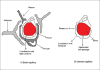
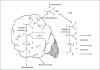
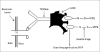
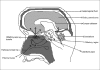
References
-
- Martin B, Robert L, Henry B, Mathiowitz E. Encyclopedia of controlled drug delivery. Vol. 1. New York: John Wiley and Sons Inc; 1999. pp. 184–210.
-
- Pardridge WM. Recent advances in blood-brain barrier transport. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1988;28:25–39. - PubMed
-
- Tamargo RJ, Brem H. Transporting therapeutics across the blood-brain barrier. Neurosurg. 1992;2:259–79.
-
- Abbott NJ, Romero IA. Transporting therapeutics across the blood-brain barrier. Mol Med Today. 1996;3:106–13. - PubMed
-
- Gelperina SE, Khalansky AS, Skidan IN, Smirnova ZS, Bobruskin AI, Severin SE, et al. Toxicological studies of doxorubicin bound to polysorbate 80-coated poly (butyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles in healthy rats and rats with intracranial glioblastoma. Toxicol Lett. 2002;126:131–41. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
