Development of biodegradable starch microspheres for intranasal delivery
- PMID: 20046707
- PMCID: PMC2792480
- DOI: 10.4103/0250-474X.41450
Development of biodegradable starch microspheres for intranasal delivery
Abstract
Domperidone microspheres for intranasal administration were prepared by emulsification crosslinking technique. Starch a biodegradable polymer was used in preparation of microspheres using epichlorhydrine as cross-linking agent. The formulation variables were drug concentration and polymer concentration and batch of drug free microsphere was prepared for comparisons. All the formulations were evaluated for particle size, morphological characteristics, percentage drug encapsulation, equilibrium swelling degree, percentage mucoadhesion, bioadhesive strength, and in vitro diffusion study using nasal cell. Spherical microspheres were obtained in all batches with mean diameter in the range of above 22.8 to 102.63 mum. They showed good mucoadhesive property and swelling behaviour. The in vitro release was found in the range of 73.11% to 86.21%. Concentration of both polymer and drug affect in vitro release of drug.
Keywords: Microspheres; bioadhesive; crosslinking; domperidone; mucoadhesion; nasal drug delivery; starch.
Figures


 , PS2
, PS2  and PS 3
and PS 3  containing different concentrations of starch.
containing different concentrations of starch.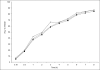
 , DS2
, DS2  and DS3
and DS3  containing different concentrations of domperidone.
containing different concentrations of domperidone.Similar articles
-
Preparation and in vitro characterization of mucoadhesive hydroxypropyl guar microspheres containing amlodipine besylate for nasal administration.Indian J Pharm Sci. 2011 Nov;73(6):608-14. doi: 10.4103/0250-474X.100233. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2011. PMID: 23112393 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan-based mucoadhesive microspheres of clarithromycin as a delivery system for antibiotic to stomach.Curr Drug Deliv. 2005 Jul;2(3):235-42. doi: 10.2174/1567201054367995. Curr Drug Deliv. 2005. PMID: 16305425
-
Gellan gum-based mucoadhesive microspheres of almotriptan for nasal administration: Formulation optimization using factorial design, characterization, and in vitro evaluation.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2014 Oct;6(4):267-77. doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.142959. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2014. PMID: 25400410 Free PMC article.
-
Microencapsulation of protein drugs for drug delivery: strategy, preparation, and applications.J Control Release. 2014 Nov 10;193:324-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.09.003. Epub 2014 Sep 10. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 25218676 Review.
-
Nasal route and drug delivery systems.Pharm World Sci. 2004 Jun;26(3):137-42. doi: 10.1023/b:phar.0000026823.82950.ff. Pharm World Sci. 2004. PMID: 15230360 Review.
Cited by
-
Polysaccharide-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Imaging and Gene Therapy.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:959175. doi: 10.1155/2015/959175. Epub 2015 May 19. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26078971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges and Opportunities of Deferoxamine Delivery for Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease, and Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Mol Pharm. 2021 Feb 1;18(2):593-609. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00474. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Mol Pharm. 2021. PMID: 32926630 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- lllum LJ. Nasal drug delivery-possibilities, problems and solution. J Control Release. 2003;87:187–98. - PubMed
-
- Aurora J. Development of nasal delivery system: A review. Drug Deliv Technol. 2002;2(7):70–3.
-
- Turker S, Anur E, Ozer Y. Nasal route and drug delivery system. Pharm World Sci. 2004;26:137–42. - PubMed
-
- Dondeti P, Zia H, Needham TE. Bioadhesive and formulation parameters affecting nasal absorption. Int J Pharm. 1996;127:115–33.
-
- Wade A, Weller PJ. A Handbook of pharmaceutical excipients, A joint publication of the American Pharma. Association and the Pharma. Great Britain: Society of Great Britain; 1994. pp. 289–95.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
