Design and development of mixed film of pectin: ethyl cellulose for colon specific drug delivery of sennosides and triphala
- PMID: 20046742
- PMCID: PMC2792520
- DOI: 10.4103/0250-474X.42998
Design and development of mixed film of pectin: ethyl cellulose for colon specific drug delivery of sennosides and triphala
Abstract
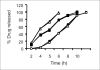
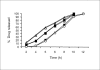
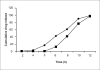
The present study was aimed at developing colon specific drug delivery system for sennosides and Triphala. These drugs are reputed Ayurvedic medicines for constipation in India. The proposed device explored the application of pectin and ethyl cellulose as a mixed film for colon specific delivery. This mixed film was prepared using non-aqueous solvents like acetone and isopropyl alcohol. A 32 factorial design was adopted to optimize the formulation variables like, ratio of ethyl cellulose to pectin (X1) and coat weight (X2). The rate and extent of drug release were found to be related to the thickness and the ratio of pectin to ethyl cellulose within the film. Statistical treatments to the drug release data revealed that the X1 variable was more important than X2. Under simulated colonic conditions, drug release was more pronounced from coating formulations containing higher proportions of pectin. The surface of the device was coated with Eudragit S100 to ensure that the device was more pH dependent and trigger the drug release only at higher pH. The final product is expected to have the advantage of being biodegradable and pH dependant. This type of a film effectively releases the drug while maintaining its integrity.
Keywords: Sennosides; Triphala; colonic drug delivery; ethyl cellulose; film coating; pectin.
Figures

References
-
- Anonymous. The Ayurvedic Formulary of India, Part I. 1st ed. Delhi: Govt. of India, Ministry of Health and Family Planning, Dept of Health; 1978. p. 85.
-
- Fairbairn JW. The active constituents of the vegetable purgatives containing anthracene derivatives. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1949;1:683–6. - PubMed
-
- Franz G. The Senna drug and its chemistry. Pharmacology. 1993;47:2–6. - PubMed
-
- Kirtikar KR, Basu BD. Indian Medicinal Plants. 2nd ed. Vol. II. Allahabad: L.M. Basu; 1933.
-
- CSIR. New Delhi: PID; 1993. The Wealth of India.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
