The temporal dynamics of implicit processing of non-letter, letter, and word-forms in the human visual cortex
- PMID: 20046826
- PMCID: PMC2796900
- DOI: 10.3389/neuro.09.056.2009
The temporal dynamics of implicit processing of non-letter, letter, and word-forms in the human visual cortex
Abstract
The decoding of visually presented line segments into letters, and letters into words, is critical to fluent reading abilities. Here we investigate the temporal dynamics of visual orthographic processes, focusing specifically on right hemisphere contributions and interactions between the hemispheres involved in the implicit processing of visually presented words, consonants, false fonts, and symbolic strings. High-density EEG was recorded while participants detected infrequent, simple, perceptual targets (dot strings) embedded amongst a of character strings. Beginning at 130 ms, orthographic and non-orthographic stimuli were distinguished by a sequence of ERP effects over occipital recording sites. These early latency occipital effects were dominated by enhanced right-sided negative-polarity activation for non-orthographic stimuli that peaked at around 180 ms. This right-sided effect was followed by bilateral positive occipital activity for false-fonts, but not symbol strings. Moreover the size of components of this later positive occipital wave was inversely correlated with the right-sided ROcc180 wave, suggesting that subjects who had larger early right-sided activation for non-orthographic stimuli had less need for more extended bilateral (e.g., interhemispheric) processing of those stimuli shortly later. Additional early (130-150 ms) negative-polarity activity over left occipital cortex and longer-latency centrally distributed responses (>300 ms) were present, likely reflecting implicit activation of the previously reported 'visual-word-form' area and N400-related responses, respectively. Collectively, these results provide a close look at some relatively unexplored portions of the temporal flow of information processing in the brain related to the implicit processing of potentially linguistic information and provide valuable information about the interactions between hemispheres supporting visual orthographic processing.
Keywords: ERPs; visual cortex; visual orthography; word reading.
Figures
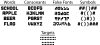

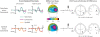


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

