Inhibition of transcription by platinum antitumor compounds
- PMID: 20046924
- PMCID: PMC2752884
- DOI: 10.1039/b907567d
Inhibition of transcription by platinum antitumor compounds
Abstract
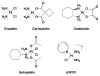
Cisplatin, carboplatin, and oxaliplatin are three FDA-approved members of the platinum anticancer drug family. These compounds induce apoptosis in tumor cells by binding to nuclear DNA, forming a variety of structural adducts and triggering cellular responses, one of which is the inhibition of transcription. In this report we present (i) a detailed review of the structural investigations of various Pt-DNA adducts and the effects of these lesions on global DNA geometry; (ii) research detailing inhibition of cellular transcription by Pt-DNA adducts; and (iii) a mechanistic analysis of how DNA structural distortions induced by platinum damage may inhibit RNA synthesis in vivo. A thorough understanding of the molecular mechanism of action of platinum antitumor agents will aid in the development of new compounds in the family.
Figures

References
-
- Loehrer PJ, Einhorn LH. Ann Intern Med. 1984;100:704–713. - PubMed
-
- Keys HM, Bundy BN, Stehman FB, Muderspach LI, Chafe WE, Suggs CL, III, Walker JL, Gersell D. New Eng J Med. 1999;340:1154–1161. - PubMed
-
- Morris M, Eifel PJ, Lu J, Grigsby PW, Levenback C, Stevens RE, Rotman M, Gershenson DM, Mutch DG. New Eng J Med. 1999;340:1137–1143. - PubMed
-
- Bosl GJ, Bajorin DF, Sheinfeld J, Motzer RJ, Chaganti RSK. In: Cancer: Principles & practice of oncology. 6. DeVita VT Jr, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA, editors. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2001. pp. 1491–1518.
-
- Bosl GJ, Motzer RJ. New Eng J Med. 1997;337:242–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

