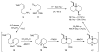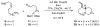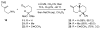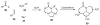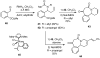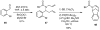Recent Applications of Imines as Key Intermediates in the Synthesis of Alkaloids and Novel Nitrogen Heterocycles
- PMID: 20046937
- PMCID: PMC2723779
- DOI: 10.1351/PAC-CON-08-07-03
Recent Applications of Imines as Key Intermediates in the Synthesis of Alkaloids and Novel Nitrogen Heterocycles
Abstract
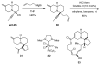
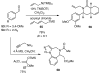
One of the major challenges in contemporary synthetic organic chemistry is the design and development of new tactics and strategies and their application to concise and efficient syntheses of biologically active natural products. Strategies that utilize reactions that enable the rapid assembly of the skeletal framework of such targets are thus especially attractive. In this context, we have developed novel applications of imine chemistry in Mannich and related reactions, cascade processes, and multicomponent reactions to rapidly assemble structural subunits common to diverse families of alkaloids. The practical utility of these chemistries is evidenced by their use in the execution of facile total syntheses of (±)-epilupinine (1), (±)-tashiromine (2), (-)-epimyrtine (3), and (±)-roelactamine (4) as well as other nitrogen heterocycles of potential biological interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cascade iminium ion reactions for the facile synthesis of quinolizidines. Concise syntheses of (+/-)-epilupinine and (-)-epimyrtine.Org Lett. 2005 May 12;7(10):2031-3. doi: 10.1021/ol050544b. Org Lett. 2005. PMID: 15876047
-
Brønsted-acid-catalyzed asymmetric multicomponent reactions for the facile synthesis of highly enantioenriched structurally diverse nitrogenous heterocycles.Acc Chem Res. 2011 Nov 15;44(11):1156-71. doi: 10.1021/ar2000343. Epub 2011 Jul 29. Acc Chem Res. 2011. PMID: 21800828
-
Synthesis of Diverse Heterocyclic Scaffolds via Tandem Additions to Imine Derivatives and Ring-Forming Reactions.Tetrahedron. 2009 Sep 15;65(33):6454-6469. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2009.05.009. Tetrahedron. 2009. PMID: 20625454 Free PMC article.
-
N-tert-Butanesulfinyl imines in the asymmetric synthesis of nitrogen-containing heterocycles.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2021 May 12;17:1096-1140. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.17.86. eCollection 2021. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2021. PMID: 34093879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of the vinylogous Mannich reaction as a key construction for alkaloid synthesis.Acc Chem Res. 2002 Oct;35(10):895-904. doi: 10.1021/ar950230w. Acc Chem Res. 2002. PMID: 12379142 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of New 5-Aryl-benzo[f][1,7]naphthyridines via a Cascade Process (Ugi-3CR/Intramolecular Aza-Diels-Alder Cycloaddition)/Aromatization.Molecules. 2018 Aug 14;23(8):2029. doi: 10.3390/molecules23082029. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30110915 Free PMC article.
-
The [3+2] Annulation of CF3-Ketimines by Re Catalysis: Access to CF3-Containing Amino Heterocycles and Polyamides.iScience. 2020 Oct 20;23(11):101705. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101705. eCollection 2020 Nov 20. iScience. 2020. PMID: 33196028 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the chemistry of imine-based multicomponent reactions (MCRs).Tetrahedron. 2011 Oct 28;67(43):8213-8228. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2011.07.020. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Tetrahedron. 2011. PMID: 32287421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mild, Redox-Neutral Alkylation of Imines Enabled by an Organic Photocatalyst.ACS Catal. 2017 Mar 3;7(3):1766-1770. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b03665. Epub 2017 Feb 6. ACS Catal. 2017. PMID: 28367354 Free PMC article.
-
Stereoselective, Multicomponent Approach to Quaternary Substituted Hydroindole Scaffolds.Org Lett. 2020 Jul 2;22(13):5079-5084. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c01650. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Org Lett. 2020. PMID: 32610919 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
For reviews of N-alkyl iminium ions, see: Blumenkopf TA, Overman LE. Chem Rev. 1986;86:857.Kleinman EF, Volkmann RA. In: Comp Org Syn. Trost BM, editor. 1991. p. 975.Royer J, Bonin M, Micouin L. Chem Rev. 2004;104:2311.For reviews of N-acyl iminium ions, see: Speckamp WN, Moolenaar MJ. Tetrahedron. 2000;56:3817.Maryanoff BE, Zhang HC, Cohen JH, Turchi IJ, Maryanoff CA. Chem Rev. 2004;104:1431.For a review of vinylogous Mannich reactions, see: Martin SF. Acc Chem Res. 2002;35:895.
-
-
-
For selected examples, see: Martin SF, Benage B, Geraci LS, Hunter JE, Mortimore M. J Am Chem Soc. 1991;113:6161.Martin SF, Clark CC, Corbett JW. J Org Chem. 1995;60:3236.Ito M, Clark CC, Mortimore M, Goh JB, Martin SF. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:8003.Liras S, Lynch CL, Fryer AM, Vu BT, Martin SF. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:5918.Reichelt A, Bur SK, Martin SF. Tetrahedron. 2002;58:6323.Deiters A, Chen K, Eary CT, Martin SF. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:4541.Martin SF, Neipp CE. J Org Chem. 2003;68:8867.Washburn DG, Heidebrecht RW, Jr, Martin SF. Org Lett. 2003;5:3523.Rudolph AC, Machauer R, Martin SF. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004;45:4895.Simila STM, Martin SF. J Org Chem. 2007;72:5342.
-
-
-
For a preliminary account of this work, see: Amorde SM, Judd AS, Martin SF. Org Lett. 2005:2031.
-
-
-
For a preliminary account of this work, see: Sunderhaus JD, Dockendorff C, Martin SF. Org Lett. 2007;9:4223. See also references therein for related strategies for rapid assembly of functionalized heterocycles.
-
-
- Wasserman HH, Vu CB, Cook JD. Tetrahedron. 1992;48:2101.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources