Early Feeding Abilities in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Parental Report Study
- PMID: 20046974
- PMCID: PMC2688002
Early Feeding Abilities in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Parental Report Study
Abstract
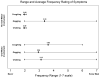
PURPOSE: The goals of this study were to 1) describe the feeding skills of young children with cerebral palsy (CP); and 2) elucidate the type and severity of feeding problems for children with and without oral-motor involvement. METHOD: Parents of 37 children (16 females, 21 males) with CP, who ranged in age from 11-58 months (mean age = 41 months), completed questionnaires regarding their child's past and current feeding abilities. Children were also clinically evaluated to determine whether each had evidence of oral-motor involvement. RESULTS: Children with CP and oral-motor involvement had significantly more difficulty with self-feeding, increased frequency of coughing and choking, increased prevalence of swallowing evaluation and feeding therapy, and were introduced to solid food at a later age relative to children with CP who did not have oral-motor involvement. Both groups of children were similar in their history of tube feeding, bottle feeding, difficulty with solid foods, use of adaptive equipment, duration of mealtimes, and presence of choking, coughing, and gagging. CONCLUSIONS: Children with and without oral-motor involvement initially presented with similar feeding difficulties. However, feeding problems appeared to resolve to a greater extent in children without oral-motor involvement. The difficulties identified early in life, for children with oral-motor involvement, appeared to persist with development.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Oropharyngeal dysphagia in preschool children with cerebral palsy: oral phase impairments.Res Dev Disabil. 2014 Dec;35(12):3469-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2014.08.029. Epub 2014 Sep 14. Res Dev Disabil. 2014. PMID: 25213472
-
Longitudinal changes in feeding among children with cerebral palsy between the ages of 4 and 7 years.Dev Neurorehabil. 2011;14(4):191-8. doi: 10.3109/17518423.2011.568467. Dev Neurorehabil. 2011. PMID: 21732803 Free PMC article.
-
[Oral motor dysfunction, feeding problems and nutritional status in children with cerebral palsy].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2004 Oct;42(10):765-8. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 16221348 Chinese.
-
Feeding and swallowing dysfunction in genetic syndromes.Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2008;14(2):147-57. doi: 10.1002/ddrr.19. Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646013 Review.
-
Prevalence of drooling, swallowing, and feeding problems in cerebral palsy across the lifespan: a systematic review and meta-analyses.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2019 Nov;61(11):1249-1258. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.14316. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31328797
Cited by
-
Intra-partum fever and cerebral palsy in Khartoum, Sudan.BMC Res Notes. 2013 Apr 24;6:163. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-6-163. BMC Res Notes. 2013. PMID: 23618409 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal cohort protocol study of oropharyngeal dysphagia: relationships to gross motor attainment, growth and nutritional status in preschool children with cerebral palsy.BMJ Open. 2012 Aug 13;2(4):e001460. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2012-001460. Print 2012. BMJ Open. 2012. PMID: 22893668 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Food Texture Modification among Individuals with Cerebral Palsy: The Challenges among Cerebral Palsy Families.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 9;14(24):5241. doi: 10.3390/nu14245241. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36558401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Swallowing and Motor Speech Skills in Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: Novel Findings From a Preliminary Cross-Sectional Study.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2022 Sep 12;65(9):3300-3315. doi: 10.1044/2022_JSLHR-22-00091. Epub 2022 Aug 11. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2022. PMID: 35952392 Free PMC article.
-
Anthropometric Parameters of Nutritional Status in Children with Cerebral Palsy.Mater Sociomed. 2017 Mar;29(1):68-72. doi: 10.5455/msm.2017.29.68-72. Mater Sociomed. 2017. PMID: 28484358 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics, Committee on Children with Disabilities. Developmental Surveillance and Screening of Infants and Young Children. Pediatrics. 2001;108(1):192–196. - PubMed
-
- Arvedson JC. Management of Swallowing Problems. In: Arvedson JC, Brodsky L, editors. Pediatric Swallowing and Feeding: Assessment and Management. San Diego, CA: Singular Publishing Group; 1993. p. 363.
-
- Arvedson JC, Brodsky L. Pediatric Swallowing and Feeding. Albany, NY: Singular Publishing Group; 2002.
-
- Boyle CA, Decoufle P, Yeargin-Allsopp M. Prevalence and health impact of developmental disabilities in US children. Pediatrics. 1994;93(3):399–403. - PubMed
-
- Dahl M, Thommessen M, Rasmussen M, Selberg T. Feeding and nutritional characteristics in children with moderate of severe cerebral palsy. Acta Pædiatr. 1996;85:697–701. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
