Discoveries from the Abyss: The Abyssomicins and Their Total Synthesis
- PMID: 20047014
- PMCID: PMC2677807
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0028-1083259
Discoveries from the Abyss: The Abyssomicins and Their Total Synthesis
Abstract
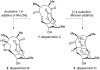
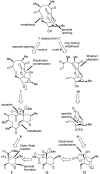
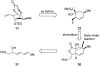
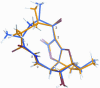
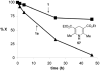
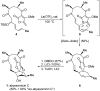
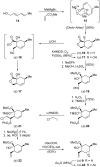
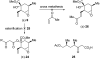
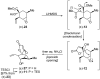
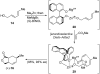
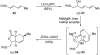
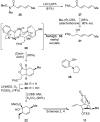
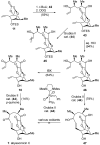
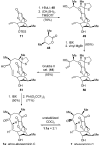
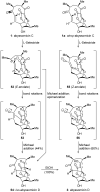
Abyssomicin C is a recently discovered antibiotic with promising antibacterial activity, high structural complexity, and a novel mechanism of action. We give an account of our abyssomicin campaign and some of the discoveries that were borne of our total synthesis efforts, including a new Lewis acid-templated Diels-Alder reaction, the previously undescribed atrop-abyssomicin C, a facile Brønsted acid-catalyzed isomerization of abyssomicin C, and clarification of the likely biosynthetic origin of abyssomicin D.
Figures


References
-
- Riedlinger J, Reicke A, Zähner H, Krismer B, Bull AT, Maldonado LA, Ward AC, Goodfellow M, Bister B, Bischoff D, Süssmuth RD, Fiedler H-P. J. Antibiot. 2004;57:271. - PubMed
- Bister B, Bischoff D, Ströbele M, Riedlinger J, Riecke A, Wolter F, Bull AT, Zähner H, Fiedler H-P, Süssmuth RD. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004;43:2574. - PubMed
-
- Walsh CT, Liu J, Rusnak F, Sakaitani M. Chem. Rev. 1990;90:1105.
-
- Zapf CW, Harrison BA, Drahl C, Sorensen EJ. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005;44:6533. - PubMed
-
-
For selected reviews on the Diels-Alder reaction and its applications to total synthesis, see:Corey EJ. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002;41:1650.Nicolaou KC, Snyder SA, Montagnon T, Vassilikogiannakis G. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002;41:1668.
-
-
- Snider BB, Zou Y. Org. Lett. 2005;7:4939. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
