Preclinical evaluation of a monoclonal antibody (3C6) specific for prostate-specific membrane antigen
- PMID: 20047017
- PMCID: PMC2678849
- DOI: 10.2174/1874471010902010009
Preclinical evaluation of a monoclonal antibody (3C6) specific for prostate-specific membrane antigen
Abstract
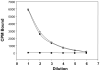
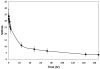
Better tumor markers are needed for early diagnosis and staging of prostate cancer, and for monitoring therapeutic response than the currently used prostate specific antigen (PSA). Prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is highly expressed on the surface of prostatic epithelial cells making it a good target for prostate cancer. In this study, mAb 3C6, specific for the extracellular epitope of PSMA, was evaluated both in vitro and in vivo for PSMA-targeting. Immunoreactivity and specificity of mAb 3C6 was evaluated by flow cytometry using prostate cell lines expressing PSMA such as LNCaP and 22Rv1 and a cell line, DU145, that expresses very little PSMA. 3C6 was conjugated with the acyclic CHX-A" DTPA chelate, radiolabeled with (111)In, and its in vitro and in vivo properties were assessed. The biodistribution of the radioimmunoconjugate evaluated in athymic mice bearing xenografts of three human prostate carcinoma cell lines shows high uptake after 72 hr in LNCaP tumors (%ID/g 22.93 +/- 6.32) and 22Rv1 (%ID/g 10.44 +/- 2.32) in contrast to low uptake by the DU145 tumors (%ID/g 4.27 +/- 0.37). Planar gamma-scintigraphic images obtained for xenografted tumor bearing mice demonstrated targeting for PSMA positive tumors suggesting possible applications in imaging and for targeted radiation therapy.
Figures



References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:43. - PubMed
-
- Catalona WJ, Richie JP, Ahmann FR, Hudson MA, Scardino PT, Flanigan RC, deKernion JB, Ratliff TL, Kavoussi LR, Dalkin BL. Comparison of digital rectal examination and serum prostate specific antigen in the early detection of prostate cancer: results of a multicenter clinical trial of 6,630 men. J. Urol. 1994;151:1283. - PubMed
-
- Murphy GP, Barren RJ, Erickson SJ, Bowes VA, Wolfert RL, Bartsch G, Klocker H, Pointner J, Reissigl A, McLeod DG, Douglas T, Morgan T, Kenny GM, Ragde H, Boynton AL, Holmes EH. Evaluation and comparison of two new prostate carcinoma markers. Free-prostate specific antigen and prostate specific membrane antigen. Cancer. 1996;78:809. - PubMed
-
- Thompson IM, Pauler DK, Goodman PJ, Tangen CM, Lucia MS, Parnes HL, Minasian LM, Ford LG, Lippman SM, Crawford ED, Crowley JJ, Coltman CA. Prevalence of prostate cancer among men with a prostate-specific antigen level < or = 4.0 ng per milliliter. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;350:2239. - PubMed
-
- Myrtle JF. Normal levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) In: Catalona WJ, Coffey DS, Karr JP, editors. Clinical aspects of prostate cancer: assessment of new diagnostic and management procedures. Elsevier; New York: 1989. pp. 183–189.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
