A Longitudinal Examination of Physiological Regulation in Cocaine-Exposed Infants Across the First 7 Months of Life
- PMID: 20047018
- PMCID: PMC2679498
- DOI: 10.1080/15250000802569660
A Longitudinal Examination of Physiological Regulation in Cocaine-Exposed Infants Across the First 7 Months of Life
Abstract
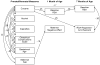
This study examined the association between prenatal exposure to cocaine and physiological regulation across the first 7 months of age. Measures of respiratory sinus arrhythmia (RSA) were obtained from 169 (82 cocaine-exposed and 87 nonexposed) infants during baseline periods at 1 month and 7 months of age and during tasks designed to elicit positive and negative affect at 7 months of age. After controlling for maternal age, gestational age, and obstetrical risk, structural equation modeling indicated that the association between prenatal exposure to cocaine and baseline RSA at 7 months of age was direct even in the presence of an indirect effect through baseline RSA at 1 month of age. There were no indirect effects through maternal affect during mother-infant interactions assessed at 1 month of age. Analyses also indicated a direct association between prenatal exposure to cocaine and RSA regulation to negative affect at 7 months of age.
Figures


References
-
- Alessandri SM, Sullivan MW, Imaizumi S, Lewis M. Learning and emotional responsivity in cocaine-exposed infants. Developmental Psychology. 1993;29:989–997.
-
- Arbuckle JL. Full information estimation in the presence of incomplete data. In: Marcoulides GA, Schumacker RE, editors. Advanced structural equation modeling techniques. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc; 1996. pp. 243–277.
-
- Arbuckle JL. AMOS users’ guide (Version 4.0) Chicago: SmallWaters; 1997.
-
- Azuma SD, Chasnoff IJ. Outcome of children prenatally exposed to cocaine and other drugs: A path analysis of three-year data. Pediatrics. 1993;92:396–402. - PubMed
-
- Bard KA, Coles CD, Platzman KA, Lynch M. The effects of prenatal drug exposure, term status, and caregiving on arousal and arousal modulation in 8-week-old infants. Developmental Psychobiology. 2000;36:194–212. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

