Small molecules and stem cells. Potency and lineage commitment: the new quest for the fountain of youth
- PMID: 20047330
- PMCID: PMC2865574
- DOI: 10.1021/jm901361d
Small molecules and stem cells. Potency and lineage commitment: the new quest for the fountain of youth
Figures
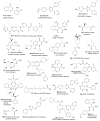
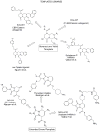
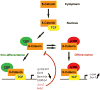
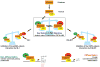
References
-
- Chambers I, Colby D, Robertson M, Nichols J, Lee S, Tweedie S, Smith A. Functional expression cloning of Nanog, a pluripotency sustaining factor in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2003;113 - PubMed
-
- Hay DC, Sutherland L, Clark J, Burdon T. Oct-4 knockdown induces similar patterns of endoderm and trophoblast differentiation markers in human and mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2004;22:225–235. - PubMed
-
- Matin MM, Walsh JR, Gokhale PJ, Draper JS, Bahrami AR, Morton I, Moore HD, Andrews PW. Specific knockdown of Oct4 and beta2-microglobulin expression by RNA interference in human embryonic stem cells and embryonic carcinoma cells. Stem Cells. 2004;22:659–668. - PubMed
-
- Mitsui K, Tokuzawa Y, Itoh H, Segawa K, Murakami M, Takahashi K, Maruyama M, Maeda M, Yamanaka S. The homeoprotein Nanog is required for maintenance of pluripotency in mouse epiblast and ES cells. Cell. 2003;113:631–642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

