Functional connectivity for somatosensory and motor cortex in spastic diplegia
- PMID: 20047510
- PMCID: PMC2804938
- DOI: 10.3109/08990220903335742
Functional connectivity for somatosensory and motor cortex in spastic diplegia
Abstract
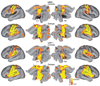
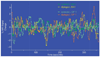
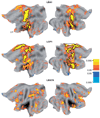
Functional connectivity (fcMRI) was analyzed in individuals with spastic diplegia and age-matched controls. Pearson correlations (r-values) were computed between resting state spontaneous activity in selected seed regions (sROI) and each voxel throughout the brain. Seed ROI were centered on foci activated by tactile stimulation of the second fingertip in somatosensory and parietal dorsal attention regions. The group with diplegia showed significantly expanded networks for the somatomotor but not dorsal attention areas. These expanded networks overran nearly all topological representations in somatosensory and motor areas despite a sROI in a fingertip focus. A possible underlying cause for altered fcMRI in the group with dipegia, and generally sensorimotor deficits in spastic diplegia, is that prenatal third trimester white-matter injury leads to localized damage to subplate neurons. We hypothesize that intracortical connections become dominant in spastic diplegia through successful competition with diminished or absent thalamocortical inputs. Similar to the effects of subplate ablations on ocular dominance columns (Kanold and Shatz, Neuron 2006;51:627-638), a spike timing-dependent plasticity model is proposed to explain a shift towards intracortical inputs.
Figures

References
-
- Back SA, Luo NL, Mallinson RA, O’Malley JP, Wallen LD, Frei B, Morrow JD, Petito CK, Roberts CT, Jr, Murdoch GH, et al. Selective vulnerability of preterm white matter to oxidative damage defined by F2-isoprostanes. Ann Neurol. 2005;58:108–120. - PubMed
-
- Bax M, Goldstein M, Rosenbaum P, Leviton A, Paneth N, Dan B, Jacobsson B, Damiano D. Proposed definition and classification of cerebral palsy, April 2005. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2005;47:571–576. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y. Excitatory actions of GABA during development: The nature of the nurture. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:728–739. - PubMed
-
- Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS. Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1995;34:537–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
