Efficacy of an olmesartan medoxomil-based treatment algorithm in patients stratified by age, race, or sex
- PMID: 20047622
- PMCID: PMC8673424
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2009.00217.x
Efficacy of an olmesartan medoxomil-based treatment algorithm in patients stratified by age, race, or sex
Abstract
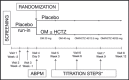
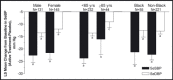
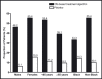
Demographic factors are known to influence the prevalence of hypertension, and evidence suggests that they may also influence the response of patients with hypertension to blood pressure (BP)-lowering therapies. To determine the effect of demographic factors on the efficacy and safety of an olmesartan medoxomil (OM)-based treatment regimen, we performed a prespecified subgroup analysis of a 12-week, randomized, placebo-controlled, titrate-to-goal study in patients with hypertension, stratifying patients into treatment groups according to age, sex, or race. After 12 weeks, OM-based therapy significantly reduced BP from baseline in blacks, non-blacks, men, women, and patients younger than 65 or 65 years and older compared with placebo, and enabled 51.9% to 79.5% of patients to achieve a BP goal of <140/90 mm Hg. The differences in BP-lowering efficacy of OM-based therapy between subgroups were not clinically significant, and treatment was generally well tolerated in all groups. This study demonstrates that an OM-based treatment algorithm is an effective and safe option for achieving recommended BP goal in patients with hypertension including blacks, non-blacks, men, women, and patients younger than 65 or 65 years and older.
Figures
References
-
- Rosamond W, Flegal K, Furie K, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics–2008 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2008;117:e25–e146. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd‐Jones DM, Evans JC, Levy D. Hypertension in adults across the age spectrum: current outcomes and control in the community. JAMA. 2005;294:466–472. - PubMed
-
- Hertz RP, Unger AN, Cornell JA, et al. Racial disparities in hypertension prevalence, awareness, and management. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165:2098–2104. - PubMed
-
- Franco OH, Peeters A, Bonneux L, et al. Blood pressure in adulthood and life expectancy with cardiovascular disease in men and women: life course analysis. Hypertension. 2005;46:280–286. - PubMed
-
- Cushman WC, Ford CE, Cutler JA, et al. Success and predictors of blood pressure control in diverse North American settings: the antihypertensive and lipid‐lowering treatment to prevent heart attack trial (ALLHAT). J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2002;4:393–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

