Compliance with the treatment of hypertension: the potential of combination therapy
- PMID: 20047629
- PMCID: PMC8673226
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2009.00200.x
Compliance with the treatment of hypertension: the potential of combination therapy
Abstract
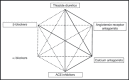
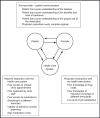
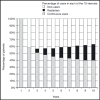
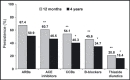
Patient adherence to antihypertensive medication is vital to ensure the successful treatment of hypertension. Low levels of adherence to and persistence with prescribed therapy are major factors leading to the current poor rates of blood pressure control among patients with hypertension. There are many reasons for nonadherence to therapy including patient-, physician-, and therapy-related factors. Poor tolerability has a detrimental effect on adherence, therefore reducing the apparent effectiveness of agents with dose-dependent side effects. Various effective combination therapies are recommended by current guidelines, eg, beta-blocker plus calcium channel blocker (CCB), angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) plus thiazide diuretic, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor plus thiazide diuretic, CCB plus thiazide diuretic, ACE inhibitor plus CCB, and ARB plus CCB, and these have the potential to increase adherence to therapy by combining a favorable tolerability profile with once-daily dosing.
Figures
References
-
- Ong KL, Cheung BM, Man YB, et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension among United States adults 1999–2004. Hypertension. 2007;49:69–75. - PubMed
-
- European Society of Hypertension Scientific Newsletter: Update on Hypertension Management, How well is hypertension controlled in Europe? http://www.eshonline.org/education/newsletter.htm. Accessed July 28, 2008.
-
- WHO . The World Health Report 2002: Risks to Health 2002. Geneva: WHO; 2002.
-
- Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, et al. 2007 Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens. 2007;25:1105–1187. - PubMed
-
- Chrysant S, Melino M, Karki S, et al. The combination of olmesartan medoxomil and amlodipine besylate in controlling high blood pressure: COACH, a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, 8‐week factorial efficacy and safety study. Clin Ther. 2008;30:587–604. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

