A versatile pH sensitive chondroitin sulfate-PEG tissue adhesive and hydrogel
- PMID: 20047758
- PMCID: PMC3430123
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.12.033
A versatile pH sensitive chondroitin sulfate-PEG tissue adhesive and hydrogel
Abstract
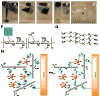
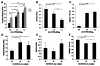
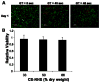
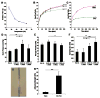
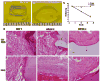
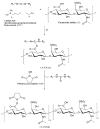
We developed a chondroitin sulfate-polyethylene glycol (CS-PEG) adhesive hydrogel with numerous potential biomedical applications. The carboxyl groups on chondroitin sulfate (CS) chains were functionalized with N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) to yield chondroitin sulfate succinimidyl succinate (CS-NHS). Following purification, the CS-NHS molecule can react with primary amines to form amide bonds. Hence, using six arm polyethylene glycol amine PEG-(NH2)6 as a crosslinker we formed a hydrogel which was covalently bound to proteins in tissue via amide bonds. By varying the initial pH of the precursor solutions, the hydrogel stiffness, swelling properties, and kinetics of gelation could be controlled. The sealing/adhesive strength could also be modified by varying the damping and storage modulus properties of the material. The adhesive strength of the material with cartilage tissue was shown to be ten times higher than that of fibrin glue. Cells encapsulated or in direct contact with the material remained viable and metabolically active. Furthermore, CS-PEG material produced minimal inflammatory response when implanted subcutaneously in a rat model and enzymatic degradation was demonstrated in vitro. This work establishes an adhesive hydrogel derived from biological and synthetic components with potential application in wound healing and regenerative medicine.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An Injectable and Instant Self-Healing Medical Adhesive for Wound Sealing.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Feb 26;12(8):9132-9140. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c01022. Epub 2020 Feb 14. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 32058692
-
Mussel-Inspired Tissue-Adhesive Hydrogel Based on the Polydopamine-Chondroitin Sulfate Complex for Growth-Factor-Free Cartilage Regeneration.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018 Aug 22;10(33):28015-28026. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b05314. Epub 2018 Aug 10. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018. PMID: 30052419
-
Synthesis and characterization of a chondroitin sulfate-polyethylene glycol corneal adhesive.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009 Mar;35(3):567-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2008.11.035. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009. PMID: 19251152
-
Tissue-Adhesive Chondroitin Sulfate Hydrogel for Cartilage Reconstruction.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021 Sep 13;7(9):4230-4243. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c01414. Epub 2021 Feb 4. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021. PMID: 33538598
-
Injectable dopamine-modified poly(ethylene glycol) nanocomposite hydrogel with enhanced adhesive property and bioactivity.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014 Oct 8;6(19):16982-92. doi: 10.1021/am504566v. Epub 2014 Sep 26. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014. PMID: 25222290 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Photo-Cross-Linkable, Injectable, and Highly Adhesive GelMA-Glycol Chitosan Hydrogels for Cartilage Repair.Adv Healthc Mater. 2023 Dec;12(32):e2302078. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202302078. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023. PMID: 37737465 Free PMC article.
-
Degradable polymer bone adhesives.Fundam Res. 2024 Feb 29;5(2):782-795. doi: 10.1016/j.fmre.2023.11.023. eCollection 2025 Mar. Fundam Res. 2024. PMID: 40242523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An adhesive bone marrow scaffold and bone morphogenetic-2 protein carrier for cartilage tissue engineering.Biomacromolecules. 2013 Mar 11;14(3):637-43. doi: 10.1021/bm301585e. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Biomacromolecules. 2013. PMID: 23320412 Free PMC article.
-
Grafting Techniques towards Production of Peptide-Tethered Hydrogels, a Novel Class of Materials with Biomedical Interest.Gels. 2015 Oct 21;1(2):194-218. doi: 10.3390/gels1020194. Gels. 2015. PMID: 30674173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ocular adhesives: Design, chemistry, crosslinking mechanisms, and applications.Biomaterials. 2019 Mar;197:345-367. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.01.011. Epub 2019 Jan 7. Biomaterials. 2019. PMID: 30690421 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ueoka C, Kaneda N, Okazaki I, Nadanaka S, Muramatsu T, Sugahara K. Neuronal cell adhesion, mediated by the heparin-binding neuroregulatory factor midkine, is specifically inhibited by chondroitin sulfate E. Structural and functional implications of the over-sulfated chondroitin sulfate. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:37407–37413. - PubMed
-
- Ronca F, Palmieri L, Panicucci P, Ronca G. Anti-inflammatory activity of chondroitin sulfate. Osteoarthr Cartil. 1998;6(Suppl A):14–21. - PubMed
-
- Campo GM, Avenoso A, Campo S, D’Ascola A, Traina P, Sama D, et al. Glycosaminoglycans modulate inflammation and apoptosis in LPS-treated chondrocytes. J Cell Biochem. 2009;106:83–92. - PubMed
-
- McGee M, Wagner WD. Chondroitin sulfate anticoagulant activity is linked to water transfer: relevance to proteoglycan structure in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003;23:1921–1927. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

