Oligometastases and oligo-recurrence: the new era of cancer therapy
- PMID: 20047860
- PMCID: PMC2813545
- DOI: 10.1093/jjco/hyp167
Oligometastases and oligo-recurrence: the new era of cancer therapy
Abstract
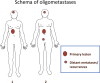
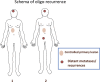
Recurrence or metastasis of cancer has been considered to occur in the last stage of the patient's life. However, the new notions of oligometastases and oligo-recurrence have been proposed and the paradigm shift in the conceptualization of cancer metastasis or cancer recurrence. Oligometastases is the state in which the patient shows distant relapse in only a limited number of regions. Local therapy such as surgery, radiotherapy and radiofrequency ablation for the relapsed sites could thus improve patient's survival. On the other hand, oligo-recurrence is a notion similar to oligometastases. However, the conditions of oligo-recurrence has a primary site of the cancer controlled, meaning that all gross recurrent or metastatic sites could be treated using local therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel insights of oligometastases and oligo-recurrence and review of the literature.Pulm Med. 2012;2012:261096. doi: 10.1155/2012/261096. Epub 2012 Aug 22. Pulm Med. 2012. PMID: 22966429 Free PMC article.
-
Oligometastases of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Review.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 7;16(4):704. doi: 10.3390/cancers16040704. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38398095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung stereotactic radiotherapy for oligometastases: comparison of oligo-recurrence and sync-oligometastases.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2016 Jul;46(7):687-91. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyw047. Epub 2016 May 9. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27162324 Free PMC article.
-
Value of high-dose radiation therapy for isolated osseous metastasis in breast cancer in terms of oligo-recurrence.Anticancer Res. 2008 Nov-Dec;28(6B):3929-31. Anticancer Res. 2008. PMID: 19192651
-
Integration of radiotherapy and immunotherapy for treatment of oligometastases.Lancet Oncol. 2019 Aug;20(8):e434-e442. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30157-3. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31364595 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel insights of oligometastases and oligo-recurrence and review of the literature.Pulm Med. 2012;2012:261096. doi: 10.1155/2012/261096. Epub 2012 Aug 22. Pulm Med. 2012. PMID: 22966429 Free PMC article.
-
Lung radiofrequency ablation: potential as a therapy to oligometastasis and oligorecurrence.Pulm Med. 2012;2012:196173. doi: 10.1155/2012/196173. Epub 2012 Oct 18. Pulm Med. 2012. PMID: 23125926 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation therapy has been shown to be adaptable for various stages of hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan 7;21(1):94-101. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i1.94. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25574082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repeated episodes of spontaneous regression/progression of cervical adenocarcinoma after adjuvant chemoradiation therapy: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2015 May 19;9:114. doi: 10.1186/s13256-015-0578-8. J Med Case Rep. 2015. PMID: 25985999 Free PMC article.
-
Radiotherapy cannot prolong overall survival of young prostate cancer patients with bone metastases.J Transl Med. 2016 Apr 27;14:102. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0868-y. J Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27116938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hellman S, Weichselbaum RR. Oligometastases. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:8–10. - PubMed
-
- Niibe Y, Kazumoto T, Toita T, Yamazaki H, Higuchi K, Ii N, et al. Frequency and characteristics of isolated para-aortic lymph node recurrence in patients with uterine cervical carcinoma in Japan: a multi-institutional study. Gynecol Oncol. 2006;103:435–8. - PubMed
-
- Niibe Y, Kenjo M, Kazumoto T, Michimoto K, Takayama M, Yamauchi C, et al. Multi-institutional study of radiation therapy for isolated para-aortic lymph node recurrence in uterine cervical carcinoma: 84 subjects of a population of more than 5000. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66:1366–9. - PubMed
-
- Niibe Y, Kuranami M, Matsunaga K, Takaya M, Kakita S, Hara T, et al. Value of high-dose radiation therapy for isolated osseous metastasis in breast cancer in terms of oligo-recurrence. Anticancer Res. 2008;28:3929–31. - PubMed
-
- Punglia RS, Morrow M, Winer EP, Harris JR. Local therapy and survival in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2399–405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

