Neuroprotection Offered by Majun Khadar, a Traditional Unani Medicine, during Cerebral Ischemic Damage in Rats
- PMID: 20047892
- PMCID: PMC3142668
- DOI: 10.1093/ecam/nep224
Neuroprotection Offered by Majun Khadar, a Traditional Unani Medicine, during Cerebral Ischemic Damage in Rats
Abstract
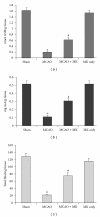
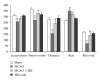
Stroke results in damages to many biochemical, molecular and behavioral deficits. Present study provides evidence of the protective efficacy of a Unani herbal medicine, Majun Khadar (MK), against cerebral ischemia-induced behavioral dysfunctions and neurochemical alterations in the hippocampus (HIP). Transient focal cerebral ischemia was induced for 2 h followed by reperfusion for 22 h in a rat model. Rats were divided into four groups: sham, middle cerebral artery occluded (MCAO), drug sham (MK; 0.816 g kg(-1) orally for 15 days) and MK pre-treated ischemic group (MK + MCAO). Levels of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants were estimated in HIP along with behavioral testing. MK pre-treatment significantly (P < .05-.001) restored the activities of glutathione peroxidase (GP×), glutathione reductase (GR), glutathione S-transferase (GST) and decreased the level of lipid peroxidation (LPO) and H2O2 content in HIP in the MK + MCAO group which were severely altered in the MCAO group. The content of glutathione (GSH), total thiols (TT) and ascorbic acid (AsA) was significantly depleted in the MCAO group; pretreatment with MK was able to restore its levels. Also in the MK + MCAO group, significant (P < .5-.001) recovery in behavioral testing by rota rod and open-field activities was seen as compared with the MCAO group. MK alone did not show any change neither in the status of various antioxidants nor behavioral functions over sham values. Although detailed studies are required for the evaluation of exact neuroprotective mechanism of MK against cerebral ischemia these preliminary experimental findings conclude that MK exhibits neuroprotective effect in cerebral ischemia by potentiating the antioxidant defense system of the brain.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Oral supplementation of Majun Baladar ameliorates antioxidant enzyme activities in cerebral ischaemic damage.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007 Oct;101(4):246-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2007.00110.x. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17845506
-
Evaluation of antioxidant and neuroprotective effect of ethanolic extract of Embelia ribes Burm in focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative stress in rats.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2008 Jun;22(3):305-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2008.00580.x. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18485149
-
Effect of dietary sesame oil as antioxidant on brain hippocampus of rat in focal cerebral ischemia.Life Sci. 2006 Oct 12;79(20):1921-8. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2006.06.017. Epub 2006 Jun 17. Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 16822528
-
Protective effect of Khamira Abresham Uood Mastagiwala against free radical induced damage in focal cerebral ischemia.J Ethnopharmacol. 2005 Jun 3;99(2):179-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2004.12.035. Epub 2005 Apr 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15894124
-
[Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract against excitotoxicity induced by NMDA receptors and mechanism thereof].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006 Sep 19;86(35):2479-84. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17156678 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Effect of Majun Baladur on life span, climbing ability, oxidative stress and dopaminergic neurons in the transgenic Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease.Heliyon. 2019 Apr 11;5(4):e01483. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01483. eCollection 2019 Apr. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31011645 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of oxysophoridine on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice.Neural Regen Res. 2013 May 25;8(15):1349-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2013.15.001. Neural Regen Res. 2013. PMID: 25206429 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Spectrometry Imaging as a New Method: To Reveal the Pathogenesis and the Mechanism of Traditional Medicine in Cerebral Ischemia.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 3;13:887050. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.887050. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35721195 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Farnsworth NR. Bioactive Compounds from Plants', (Ciba Foundation Symposium, Chicago, Illinois) Chichester, UK: Wiley; 1990. The role of ethnopharmacology in drug development; pp. 2–21. - PubMed
-
- Yousuf S, Salim S, Ahmad M, Ahmed AS, Ansari MA, Islam F. Protective effect of Khamira Abresham Uood Mastagiwala against free radical induced damage in focal cerebral ischemia. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2005;99(2):179–184. - PubMed
-
- Yousuf S, Atif F, Ahmad M, et al. Selenium plays a modulatory role against cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal damage in rat hippocampus. Brain Research. 2007;1147(1):218–225. - PubMed
-
- Saleem S, Ahmad M, Zafar KS, Ahmad AS, Islam F. Protective effect of Nardostachys jatamansi in rat cerebral ischemia. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 2003;74:481–486. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

