Site-specific chromosomal integration of large synthetic constructs
- PMID: 20047970
- PMCID: PMC2847246
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp1193
Site-specific chromosomal integration of large synthetic constructs
Abstract
We have developed an effective, easy-to-use two-step system for the site-directed insertion of large genetic constructs into arbitrary positions in the Escherichia coli chromosome. The system uses lambda-Red mediated recombineering accompanied by the introduction of double-strand DNA breaks in the chromosome and a donor plasmid bearing the desired insertion fragment. Our method, in contrast to existing recombineering or phage-derived insertion methods, allows for the insertion of very large fragments into any desired location and in any orientation. We demonstrate this method by inserting a 7-kb fragment consisting of a venus-tagged lac repressor gene along with a target lacZ reporter into six unique sites distributed symmetrically about the chromosome. We also demonstrate the universality and repeatability of the method by separately inserting the lac repressor gene and the lacZ target into the chromosome at separate locations around the chromosome via repeated application of the protocol.
Figures
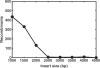




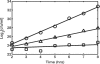
Similar articles
-
A place for everything: chromosomal integration of large constructs.Bioeng Bugs. 2010 Jul-Aug;1(4):296-9. doi: 10.4161/bbug.1.4.12386. Epub 2010 May 13. Bioeng Bugs. 2010. PMID: 21327065 Free PMC article.
-
A novel approach for Escherichia coli genome editing combining in vivo cloning and targeted long-length chromosomal insertion.J Microbiol Methods. 2016 Nov;130:83-91. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2016.08.024. Epub 2016 Aug 25. J Microbiol Methods. 2016. PMID: 27567891
-
Knock-in/Knock-out (KIKO) vectors for rapid integration of large DNA sequences, including whole metabolic pathways, onto the Escherichia coli chromosome at well-characterised loci.Microb Cell Fact. 2013 Jun 24;12:60. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-12-60. Microb Cell Fact. 2013. PMID: 23799955 Free PMC article.
-
Recombineering: genetic engineering in bacteria using homologous recombination.Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2007 Apr;Chapter 1:Unit 1.16. doi: 10.1002/0471142727.mb0116s78. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 18265390 Review.
-
Phage recombinases and their applications.Adv Virus Res. 2012;83:367-414. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394438-2.00008-6. Adv Virus Res. 2012. PMID: 22748814 Review.
Cited by
-
A strategy of gene overexpression based on tandem repetitive promoters in Escherichia coli.Microb Cell Fact. 2012 Feb 6;11:19. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-11-19. Microb Cell Fact. 2012. PMID: 22305426 Free PMC article.
-
Robust counterselection and advanced λRed recombineering enable markerless chromosomal integration of large heterologous constructs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Aug 26;50(15):8947-8960. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac649. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35920321 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of isobutanol using acetate as sole carbon source in Escherichia coli.Microb Cell Fact. 2023 Sep 27;22(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s12934-023-02197-w. Microb Cell Fact. 2023. PMID: 37759284 Free PMC article.
-
Different performance of Escherichia coli mutants with defects in the phosphoenolpyruvate: carbohydrate phosphotransferase system under low glucose condition.3 Biotech. 2019 Feb;9(2):50. doi: 10.1007/s13205-019-1584-0. Epub 2019 Jan 24. 3 Biotech. 2019. PMID: 30729074 Free PMC article.
-
Multicopy integration of mini-Tn7 transposons into selected chromosomal sites of a Salmonella vaccine strain.Microb Biotechnol. 2015 Jan;8(1):177-87. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12187. Epub 2014 Dec 9. Microb Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25488129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lin-Chao S, Bremer H. Effect of the bacterial growth rate on replication control of plasmid pBR322 in Escherichia coli. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1986;203:143–149. - PubMed
-
- Paulsson J, Ehrenberg M. Noise in a minimal regulatory network: plasmid copy number control. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2001;34:1–59. - PubMed
-
- Pedraza JM, van Oudenaarden A. Noise propagation in gene networks. Science. 2005;307:1965–1969. - PubMed
-
- Cooper S, Helmstetter CE. Chromosome replication and the division cycle of Escherichia coli B/r. J. Mol. Biol. 1968;31:519–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

