GacA-controlled activation of promoters for small RNA genes in Pseudomonas fluorescens
- PMID: 20048056
- PMCID: PMC2832403
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02014-09
GacA-controlled activation of promoters for small RNA genes in Pseudomonas fluorescens
Abstract
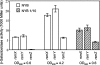
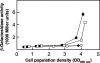
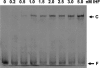
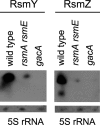
The Gac/Rsm signal transduction pathway positively regulates secondary metabolism, production of extracellular enzymes, and biocontrol properties of Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0 via the expression of three noncoding small RNAs, termed RsmX, RsmY, and RsmZ. The architecture and function of the rsmY and rsmZ promoters were studied in vivo. A conserved palindromic upstream activating sequence (UAS) was found to be necessary but not sufficient for rsmY and rsmZ expression and for activation by the response regulator GacA. A poorly conserved linker region located between the UAS and the -10 promoter sequence was also essential for GacA-dependent rsmY and rsmZ expression, suggesting a need for auxiliary transcription factors. One such factor involved in the activation of the rsmZ promoter was identified as the PsrA protein, previously recognized as an activator of the rpoS gene and a repressor of fatty acid degradation. Furthermore, the integration host factor (IHF) protein was found to bind with high affinity to the rsmZ promoter region in vitro, suggesting that DNA bending contributes to the regulated expression of rsmZ. In an rsmXYZ triple mutant, the expression of rsmY and rsmZ was elevated above that found in the wild type. This negative feedback loop appears to involve the translational regulators RsmA and RsmE, whose activity is antagonized by RsmXYZ, and several hypothetical DNA-binding proteins. This highly complex network controls the expression of the three small RNAs in response to cell physiology and cell population densities.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RsmY, a small regulatory RNA, is required in concert with RsmZ for GacA-dependent expression of biocontrol traits in Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0.Mol Microbiol. 2003 Nov;50(4):1361-79. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03774.x. Mol Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14622422
-
Genome-wide search reveals a novel GacA-regulated small RNA in Pseudomonas species.BMC Genomics. 2008 Apr 13;9:167. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-167. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18405392 Free PMC article.
-
Posttranscriptional repression of GacS/GacA-controlled genes by the RNA-binding protein RsmE acting together with RsmA in the biocontrol strain Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0.J Bacteriol. 2005 Jan;187(1):276-85. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.1.276-285.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 15601712 Free PMC article.
-
Gac/Rsm signal transduction pathway of gamma-proteobacteria: from RNA recognition to regulation of social behaviour.Mol Microbiol. 2008 Jan;67(2):241-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.06042.x. Epub 2007 Nov 28. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18047567 Review.
-
Small RNAs as regulators of primary and secondary metabolism in Pseudomonas species.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011 Jul;91(1):63-79. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3332-1. Epub 2011 May 24. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21607656 Review.
Cited by
-
Two Homologues of the Global Regulator Csr/Rsm Redundantly Control Phaseolotoxin Biosynthesis and Virulence in the Plant Pathogen Pseudomonas amygdali pv. phaseolicola 1448A.Microorganisms. 2020 Oct 6;8(10):1536. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8101536. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33036191 Free PMC article.
-
Amplifying and Fine-Tuning Rsm sRNAs Expression and Stability to Optimize the Survival of Pseudomonas brassicacerum in Nutrient-Poor Environments.Microorganisms. 2021 Jan 26;9(2):250. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9020250. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33530561 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide protein-DNA interaction site mapping in bacteria using a double-stranded DNA-specific cytosine deaminase.Nat Microbiol. 2022 Jun;7(6):844-855. doi: 10.1038/s41564-022-01133-9. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Nat Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35650286 Free PMC article.
-
The regulator FleQ both transcriptionally and post-transcriptionally regulates the level of RTX adhesins of Pseudomonas fluorescens.J Bacteriol. 2023 Sep 26;205(9):e0015223. doi: 10.1128/jb.00152-23. Epub 2023 Sep 1. J Bacteriol. 2023. PMID: 37655913 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Fluorescent Siderophore Biosynthesis and Loss of Phenazine-1-Carboxamide in Phenotypic Variant of Pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66.Front Microbiol. 2018 Apr 23;9:759. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00759. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29740409 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babitzke, P., and T. Romeo. 2007. CsrB sRNA family: sequestration of RNA-binding regulatory proteins. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 10:156-163. - PubMed
-
- Bao, Y., D. P. Lies, H. Fu, and G. P. Roberts. 1991. An improved Tn7-based system for the single-copy insertion of cloned genes into chromosomes of gram-negative bacteria. Gene 109:167-168. - PubMed
-
- Bejerano-Sagie, M., and K. B. Xavier. 2007. The role of small RNAs in quorum sensing. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 10:189-198. - PubMed
-
- Blumer, C., A. Kleefeld, D. Lehnen, M. Heintz, U. Dobrindt, G. Nagy, K. Michaelis, L. Emödy, T. Polen, R. Rachel, V. F. Wendisch, and G. Unden. 2005. Regulation of type 1 fimbriae synthesis and biofilm formation by the transcriptional regulator LrhA of Escherichia coli. Microbiology 151:3287-3298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

