Combining human and rat sequences in her-2 DNA vaccines blunts immune tolerance and drives antitumor immunity
- PMID: 20048073
- PMCID: PMC3947604
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2554
Combining human and rat sequences in her-2 DNA vaccines blunts immune tolerance and drives antitumor immunity
Erratum in
- Cancer Res. 2010 Mar 15;70(6):2569
Abstract
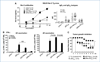
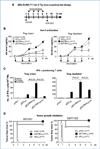
Immune tolerance to tumor-associated self-antigens poses a major challenge in the ability to mount an effective cancer vaccine response. To overcome immune tolerance to HER-2, we formulated DNA vaccines that express both human HER-2 and heterologous rat Neu sequences in separate plasmids or as single hybrid constructs that encode HER-2/Neu fusion proteins. Candidate vaccines were tested in Her-2 transgenic (Tg) mice of BALB/c (BALB), BALB/cxC57BL/6 F1 (F1), or C57BL/6 (B6) background, which exhibit decreasing immune responsiveness to HER-2. Analysis of various cocktails or hybrid vaccines defined a requirement for particular combination of HER/2/Neu sequences to effectively prime immune effector cells in HER-2 Tg mice. In B6 HER-2 Tg mice, rejection of HER-2-positive tumors protected mice from HER-2-negative tumors, providing evidence of epitope spreading. Our findings show that a strategy of combining heterologous antigen with self-antigens could produce a potent DNA vaccine that may be applicable to other tumor-associated antigens.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
W-Z. Wei: consultant/advisory board, NIH and Department of Defense. The other authors disclosed no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Hung MC, Lau YK. Basic science of HER-2/neu: a review. Semin Oncol. 1999;4(suppl 12):51–59. - PubMed
-
- Pietras RJ, Fendly BM, Chazin VR, Pegram MD, Howell SB, Slamon DJ. Antibody to HER-2/neu receptor blocks DNA repair after cisplatin in human breast and ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene. 1994;9:1829–1838. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA, et al. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989;244:707–712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

