Site-specific phosphorylation of CXCR4 is dynamically regulated by multiple kinases and results in differential modulation of CXCR4 signaling
- PMID: 20048153
- PMCID: PMC2844224
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.091173
Site-specific phosphorylation of CXCR4 is dynamically regulated by multiple kinases and results in differential modulation of CXCR4 signaling
Abstract
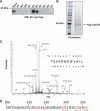
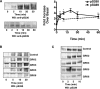
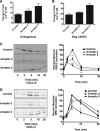
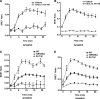
The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is a widely expressed G protein-coupled receptor that has been implicated in a number of diseases including human immunodeficiency virus, cancer, and WHIM syndrome, with the latter two involving dysregulation of CXCR4 signaling. To better understand the role of phosphorylation in regulating CXCR4 signaling, tandem mass spectrometry and phospho-specific antibodies were used to identify sites of agonist-promoted phosphorylation. These studies demonstrated that Ser-321, Ser-324, Ser-325, Ser-330, Ser-339, and two sites between Ser-346 and Ser-352 were phosphorylated in HEK293 cells. We show that Ser-324/5 was rapidly phosphorylated by protein kinase C and G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 (GRK6) upon CXCL12 treatment, whereas Ser-339 was specifically and rapidly phosphorylated by GRK6. Ser-330 was also phosphorylated by GRK6, albeit with slower kinetics. Similar results were observed in human astroglia cells, where endogenous CXCR4 was rapidly phosphorylated on Ser-324/5 by protein kinase C after CXCL12 treatment, whereas Ser-330 was slowly phosphorylated. Analysis of CXCR4 signaling in HEK293 cells revealed that calcium mobilization was primarily negatively regulated by GRK2, GRK6, and arrestin3, whereas GRK3, GRK6, and arrestin2 played a primary role in positively regulating ERK1/2 activation. In contrast, GRK2 appeared to play a negative role in ERK1/2 activation. Finally, we show that arrestin association with CXCR4 is primarily driven by the phosphorylation of far C-terminal residues on the receptor. These studies reveal that site-specific phosphorylation of CXCR4 is dynamically regulated by multiple kinases resulting in both positive and negative modulation of CXCR4 signaling.
Figures




Similar articles
-
G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 3 and Protein Kinase C Phosphorylate the Distal C-Terminal Tail of the Chemokine Receptor CXCR4 and Mediate Recruitment of β-Arrestin.Mol Pharmacol. 2017 Jun;91(6):554-566. doi: 10.1124/mol.116.106468. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Mol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28331048 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired recruitment of Grk6 and beta-Arrestin 2 causes delayed internalization and desensitization of a WHIM syndrome-associated CXCR4 mutant receptor.PLoS One. 2009 Dec 1;4(12):e8102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008102. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19956569 Free PMC article.
-
Selective recruitment of G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) controls signaling of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 May 1;109(18):7055-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1118359109. Epub 2012 Apr 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22509025 Free PMC article.
-
The complex nature of CXCR4 mutations in WHIM syndrome.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 5;15:1406532. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1406532. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39035006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of CXCR4 signaling.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Apr;1768(4):952-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.11.002. Epub 2006 Nov 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17169327 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HGF-induced PKCζ activation increases functional CXCR4 expression in human breast cancer cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29124. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029124. Epub 2012 Jan 5. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22242160 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between CXCR4/ACKR3 and EGFR Signaling in Breast Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 6;23(19):11887. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911887. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233192 Free PMC article.
-
IL-24 inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by disrupting the SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling axis.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 16;10(3):e0122439. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122439. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25775124 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR4-SERINE339 regulates cellular adhesion, retention and mobilization, and is a marker for poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia.Leukemia. 2014 Mar;28(3):566-76. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.201. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Leukemia. 2014. PMID: 23817178
-
Intrinsically disordered proteins play diverse roles in cell signaling.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Feb 17;20(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00821-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 35177069 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hernandez P. A., Gorlin R. J., Lukens J. N., Taniuchi S., Bohinjec J., Francois F., Klotman M. E., Diaz G. A. (2003) Nat. Genet. 34, 70–74 - PubMed
-
- Feng Y., Broder C. C., Kennedy P. E., Berger E. A. (1996) Science 272, 872–877 - PubMed
-
- Zlotnik A. (2006) Contrib. Microbiol. 13, 191–199 - PubMed
-
- Diaz G. A., Gulino A. V. (2005) Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 5, 350–355 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

