Investigational immunotherapeutics for B-cell malignancies
- PMID: 20048186
- PMCID: PMC4872311
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2009.22.8254
Investigational immunotherapeutics for B-cell malignancies
Abstract
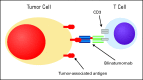
The use of rituximab-based chemoimmunotherapy regimens has remarkably improved the response rates, long-term outcomes, and quality of life of patients with B-cell malignancies. However, a substantial number of patients exhibit either primary or acquired resistance to rituximab, which suggests that novel immunotherapeutics with distinct mechanisms of action are necessary. A series of monoclonal antibodies with specificity against different surface antigens expressed on malignant B cells (eg, CD22, CD23, CD40, CD70) and novel immunotherapeutics (eg, bispecific monoclonal antibodies, small-modular immunopharmaceuticals, T-cell engagers) are currently in clinical or final preclinical stages of development. Although these agents offer reason for optimism, considerable challenges lie ahead in establishing their real clinical value, as well as in integrating them into current therapeutic algorithms for patients with B-cell malignancies. This review describes some of the most promising investigational immunotherapeutics for the treatment of B-cell malignancies.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD19 as an attractive target for antibody-based therapy.MAbs. 2012 Sep-Oct;4(5):571-7. doi: 10.4161/mabs.21338. Epub 2012 Jul 23. MAbs. 2012. PMID: 22820352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical and clinical evaluation of epratuzumab (anti-CD22 IgG) in B-cell malignancies.Oncogene. 2007 May 28;26(25):3704-13. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210370. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17530024 Review.
-
Performance of CD3xCD19 bispecific monoclonal antibodies in B cell malignancy.Leuk Lymphoma. 1995 Nov;19(5-6):381-93. doi: 10.3109/10428199509112195. Leuk Lymphoma. 1995. PMID: 8590837 Review.
-
Novel approaches to the immunotherapy of B-cell malignancies: An update.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2006 Dec;1(4):258-63. doi: 10.1007/s11899-006-0007-6. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2006. PMID: 20425321 Review.
-
Novel approaches to immunotherapy for B-cell malignancies.Curr Oncol Rep. 2004 Sep;6(5):339-47. doi: 10.1007/s11912-004-0059-5. Curr Oncol Rep. 2004. PMID: 15291974 Review.
Cited by
-
Pediatric posttransplant relapsed/refractory B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia shows durable remission by therapy with the T-cell engaging bispecific antibody blinatumomab.Haematologica. 2014 Jul;99(7):1212-9. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2013.100073. Epub 2014 Apr 11. Haematologica. 2014. PMID: 24727818 Free PMC article.
-
Relapsed Primary Cutaneous Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma, Leg Type.Indian J Dermatol. 2017 Nov-Dec;62(6):676. doi: 10.4103/ijd.IJD_700_16. Indian J Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 29263555 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Immunotherapy for B-Cell Neoplasms using T Cells expressing Chimeric Antigen Receptors: From antigen choice to clinical implementation.Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2012 Aug;12(3):273-85. doi: 10.12816/0003140. Epub 2012 Jul 15. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2012. PMID: 23269948 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and immunotoxicity assessment of immunomodulatory monoclonal antibodies.MAbs. 2010 May-Jun;2(3):233-55. doi: 10.4161/mabs.2.3.11782. Epub 2010 May 23. MAbs. 2010. PMID: 20421713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD22 EXON 12 deletion as a pathogenic mechanism of human B-precursor leukemia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Sep 28;107(39):16852-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1007896107. Epub 2010 Sep 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20841423 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Golay J, Zaffaroni L, Vaccari T, et al. Biologic response of B lymphoma cells to anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab in vitro: CD55 and CD59 regulate complement-mediated cell lysis. Blood. 2000;95:3900–3908. - PubMed
-
- Treon SP, Mitsiades C, Mitsiades N, et al. Tumor cell expression of CD59 is associated with resistance to CD20 serotherapy in patients with B-cell malignancies. J Immunother. 2001;24:263–271. - PubMed
-
- Pedersen IM, Buhl AM, Klausen P, et al. The chimeric anti-CD20 antibody rituximab induces apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells through a p38 mitogen activated protein-kinase-dependent mechanism. Blood. 2002;99:1314–1319. - PubMed
-
- Alas S, Emmanouilides C, Bonavida B. Inhibition of interleukin 10 by rituximab results in down-regulation of bcl-2 and sensitization of B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma to apoptosis. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:709–723. - PubMed
-
- Tan D, Horning SJ. Follicular lymphoma: Clinical features and treatment. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2008;22:863–882. vi. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

