Intracoronary administration of cardiac progenitor cells alleviates left ventricular dysfunction in rats with a 30-day-old infarction
- PMID: 20048209
- PMCID: PMC2814341
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.871905
Intracoronary administration of cardiac progenitor cells alleviates left ventricular dysfunction in rats with a 30-day-old infarction
Abstract
Background: Administration of cardiac progenitor cells (CPCs) 4 hours after reperfusion ameliorates left ventricular function in rats with acute myocardial infarction (MI). Clinically, however, this approach is not feasible, because expansion of autologous CPCs after acute MI requires several weeks. Therefore, we sought to determine whether CPCs are beneficial in the more clinically relevant setting of an old MI (scar).
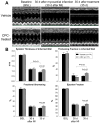
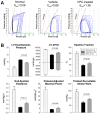
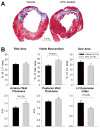
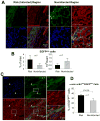
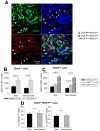
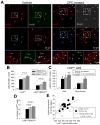
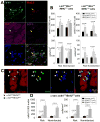
Methods and results: One month after coronary occlusion/reperfusion, rats received an intracoronary infusion of vehicle or enhanced green fluorescent protein-labeled CPCs. Thirty-five days later, CPC-treated rats exhibited more viable myocardium in the risk region, less fibrosis in the noninfarcted region, and improved left ventricular function. Cells that stained positive for enhanced green fluorescent protein that expressed cardiomyocyte, endothelial, and vascular smooth muscle cell markers were observed only in 7 of 17 treated rats and occupied only 2.6% and 1.1% of the risk and noninfarcted regions, respectively. Transplantation of CPCs was associated with increased proliferation and expression of cardiac proteins by endogenous CPCs.
Conclusions: Intracoronary administration of CPCs in the setting of an old MI produces beneficial structural and functional effects. Although exogenous CPCs can differentiate into new cardiac cells, this mechanism is not sufficient to explain the benefits, which suggests paracrine effects; among these, the present data identify activation of endogenous CPCs. This is the first report that CPCs are beneficial in the setting of an old MI when given by intracoronary infusion, the most widely applicable therapeutic approach in patients. Furthermore, this is the first evidence that exogenous CPC administration activates endogenous CPCs. These results open the door to new therapeutic applications for the use of autologous CPCs in patients with old MI and chronic ischemic cardiomyopathy.
Figures

References
-
- Wollert KC, Drexler H. Clinical applications of stem cells for the heart. Circ Res. 2005;96:151–163. - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Latif A, Bolli R, Tleyjeh IM, Montori VM, Perin EC, Hornung CA, Zuba-Surma EK, Al-Mallah M, Dawn B. Adult bone marrow-derived cells for cardiac repair: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167:989–997. - PubMed
-
- Bearzi C, Rota M, Hosoda T, Tillmanns J, Nascimbene A, De Angelis A, Yasuzawa-Amano S, Trofimova I, Siggins RW, Lecapitaine N, Cascapera S, Beltrami AP, D’Alessandro DA, Zias E, Quaini F, Urbanek K, Michler RE, Bolli R, Kajstura J, Leri A, Anversa P. Human cardiac stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:14068–14073. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beltrami AP, Barlucchi L, Torella D, Baker M, Limana F, Chimenti S, Kasahara H, Rota M, Musso E, Urbanek K, Leri A, Kajstura J, Nadal-Ginard B, Anversa P. Adult cardiac stem cells are multipotent and support myocardial regeneration. Cell. 2003;114:763–776. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 HL055757/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL076794/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-91202/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-70897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-68088/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091202/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-55757/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL074351/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL068088/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-78825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055757/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-74351/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL078825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-76794/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

