Clinical practice with antidementia and antipsychotic drugs: Audit from a geriatric clinic in India
- PMID: 20048452
- PMCID: PMC2802374
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5545.58292
Clinical practice with antidementia and antipsychotic drugs: Audit from a geriatric clinic in India
Abstract
Background: Dementia is one of the most disabling disorders afflicting the elderly, with a staggering emotional and economic impact. Antidementia agents have been used for delaying cognitive decline. Antipsychotics are commonly prescribed for behavioral symptoms associated with dementia.
Objectives: To explore the use of anti-dementing agents and antipsychotics used in patients with a diagnosis of dementia Materials and Methods: A retrospective chart review method; geriatric clinic of tertiary care setting.
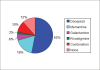
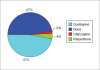
Results: The study sample included 51 consecutive patients with a diagnosis of dementia. The commonest subtype of dementia that was diagnosed was Alzheimer's disease (45%), followed by Frontotemporal dementia (25%).The commonest antidementia drug that was used was donepezil, which alone was prescribed in 27 patients (52%). The commonest antipsychotic used was quetiapine, which was used in 24 patients (47%).
Conclusions: The study found donepezil to be the most commonly prescribed antidementia drug and quetiapine to be the most commonly used antipsychotic in a tertiary care geriatric clinic, in a developing country. There is a need to study the cost-effectiveness of antidementia and antipsychotic drugs in patients with dementia, in developing countries.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Shafqat S. Alzheimer disease therapeutics: Perspectives from developing world. J Alzheimers Dis. 2008;15:285–7. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association - Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients with Alzheimer's disease and Other Dementias. Second Edition 2007. - PubMed
-
- Fillit HM, Doody RS, Binaso K, Crooks GM, Ferris SH, Farlow MR, et al. Recommendations for best practices in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease in managed care. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2006;4:S9–S24. quiz S25-8. - PubMed