Trichostatin A sensitizes cisplatin-resistant A549 cells to apoptosis by up-regulating death-associated protein kinase
- PMID: 20048748
- PMCID: PMC4002697
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2009.183
Trichostatin A sensitizes cisplatin-resistant A549 cells to apoptosis by up-regulating death-associated protein kinase
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the apoptosis-inducing effect of trichostatin A (TSA) in the human lung adenocarcinoma cisplatin-resistant cell line (A549/CDDP) and to examine whether TSA can enhance sensitivity to cisplatin treatment and the underlying molecular mechanisms of such an enhancement.
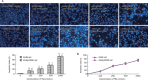
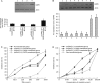
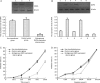
Methods: Cell viability was evaluated using the Neutral Red assay. Apoptosis was assessed using Hoechst 33258 staining and flow cytometry analysis. Protein expression was detected by Western blotting. To determine the role of Death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) in TSA-induced apoptosis in the A549/CDDP cell line, cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1(+)-DAPK, which has a higher expression level of DAPK compared to endogenous expression, and DAPK activity was inhibited by both over-expression C-terminal fragment of DAPK which may competitive binding DAPK substrates to inhibit the function of DAPK and RNA interference.
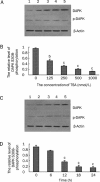
Results: TSA induced apoptosis in both A549 cells and A549/CDDP cells. TSA enhanced the sensitivity of A549/CDDP cells to cisplatin, along with concomitant DAPK up-regulation. When DAPK was over-expressed, A549/CDDP cells became sensitive to cisplatin and the cytotoxicity of TSA could be increased. Moreover, the cytotoxicity of TSA could be alleviated by inhibition of DAPK activity by the expression of a recombinant C-terminal fragment of DAPK or RNA interference.
Conclusion: TSA induced sensitivity to cisplatin treatment in cisplatin-resistant A549 cells. The up-regulation of DAPK is one of the mechanisms mediating sensitization to TSA-induced apoptosis in cisplatin-resistant cells.
Figures




References
-
- Pignon JP, Tribodet H, Scagliotti GV, Douillard JY, Shepherd FA, Stephens RJ.et al. Lung adjuvant cisplatin evaluation: a pooled analysis by the LACE Collaborative Group J Clin Oncol 2008263552–9. - PubMed
-
- Bria E, Cuppone F, Cecere FL, Milella M, Nisticò C, Cognetti F.et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer J Thorac Oncol 20072S7–11. - PubMed
-
- Winton T, Livingston R, Johnson D, Rigas J, Johnston M, Butts C.et al. Vinorelbine plus cisplatin vs observation in resected non-small-cell lung cancer N Engl J Med 20053522589–97. - PubMed
-
- Douillard JY, Rosell R, De Lena M, Carpagnano F, Ramlau R, Gonzáles-Larriba JL.et al. Adjuvant vinorelbine plus cisplatin versus observation in patients with completely resected stage IB-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (Adjuvant Navelbine International Trialist Association ANITA): a randomised controlled trial Lancet Oncol 20067719–27. - PubMed
-
- Stewart DJ. Mechanisms of resistance to cisplatin and carboplatin. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2007;63:12–31. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

