LDLR expression and localization are altered in mouse and human cell culture models of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 20049331
- PMCID: PMC2797391
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008556
LDLR expression and localization are altered in mouse and human cell culture models of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a chronic neurodegenerative disorder and the most common form of dementia. The major molecular risk factor for late-onset AD is expression of the epsilon-4 allele of apolipoprotein E (apoE), the major cholesterol transporter in the brain. The low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) has the highest affinity for apoE and plays an important role in brain cholesterol metabolism.
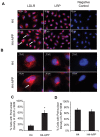
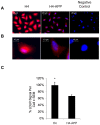
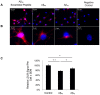
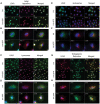
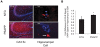
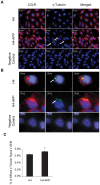
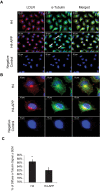
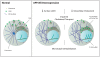
Methodology/principal findings: Using RT-PCR and western blotting techniques we found that over-expression of APP caused increases in both LDLR mRNA and protein levels in APP transfected H4 neuroglioma cells compared to H4 controls. Furthermore, immunohistochemical experiments showed aberrant localization of LDLR in H4-APP neuroglioma cells, Abeta-treated primary neurons, and in the PSAPP transgenic mouse model of AD. Finally, immunofluorescent staining of LDLR and of gamma- and alpha-tubulin showed a change in LDLR localization preferentially away from the plasma membrane that was paralleled by and likely the result of a disruption of the microtubule-organizing center and associated microtubule network.
Conclusions/significance: These data suggest that increased APP expression and Abeta exposure alters microtubule function, leading to reduced transport of LDLR to the plasma membrane. Consequent deleterious effects on apoE uptake and function will have implications for AD pathogenesis and/or progression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Glenner GG, Wong CW. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984;120:885–890. - PubMed
-
- Potter H, Wefes IM, Nilsson LN. The inflammation-induced pathological chaperones ACT and apo-E are necessary catalysts of Alzheimer amyloid formation. Neurobiol Aging. 2001;22:923–930. - PubMed
-
- Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel D, George-Hyslop PH, Pericak-Vance MA, et al. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1993;43:1467–1472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

