Nucleolin as cell surface receptor for tumor necrosis factor-alpha inducing protein: a carcinogenic factor of Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 20049476
- PMCID: PMC11828327
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-009-0733-y
Nucleolin as cell surface receptor for tumor necrosis factor-alpha inducing protein: a carcinogenic factor of Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
Purpose: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inducing protein (Tipalpha) is a unique carcinogenic factor released from Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). Tipalpha specifically binds to cells and is incorporated into cytosol and nucleus, where it strongly induces expression of TNF-alpha and chemokine genes mediated through NF-kappaB activation, resulting in tumor development. To elucidate mechanism of action of Tipalpha, we studied a binding protein of Tipalpha in gastric epithelial cells.
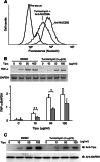
Methods: Tipalpha binding protein was found in cell lysates of mouse gastric cancer cell line MGT-40 by FLAG-pull down assay and identified to be cell surface nucleolin by flow cytometry using anti-nucleolin antibody. Incorporation of Tipalpha into the cells was determined by Western blotting and expression of TNF-alpha gene was quantified by RT-PCR.
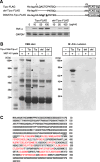
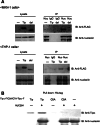
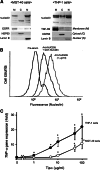
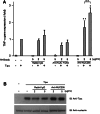
Results: Nucleolin was co-precipitated with Tipalpha-FLAG, but not with del-Tipalpha-FLAG (an inactive mutant). After treatment with Tipalpha-FLAG, incorporated Tipalpha was co-immunoprecipitated with endogenous nucleolin using anti-nucleolin antibody. The direct binding of Tipalpha to recombinant His-tagged nucleolin fragment (284-710) was also confirmed. Although nucleolin is an abundant non-ribosomal protein of the nucleolus, we found that nucleolin is present on the cell surface of MGT-40 cells. Pretreatment with anti-nucleolin antibody enhanced Tipalpha-incorporation into the cells through nucleolin internalization. In addition, pretreatment with tunicamycin, an inhibitor of N-glycosylation, decreased the amounts of cell surface nucleolin and inhibited both internalization of Tipalpha and expression of TNF-alpha gene.
Conclusions: All the results indicate that nucleolin acts as a receptor for Tipalpha and shuttles Tipalpha from cell surface to cytosol and nuclei. These findings provide a new mechanistic insight into gastric cancer development with Tipalpha.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New tumor necrosis factor-alpha-inducing protein released from Helicobacter pylori for gastric cancer progression.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2005 May;131(5):305-13. doi: 10.1007/s00432-004-0652-x. Epub 2004 Dec 23. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2005. PMID: 15616827 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori-secreting protein Tipalpha is a potent inducer of chemokine gene expressions in stomach cancer cells.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2007 May;133(5):287-96. doi: 10.1007/s00432-006-0169-6. Epub 2006 Nov 25. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17393199 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-surface nucleolin acts as a central mediator for carcinogenic, anti-carcinogenic, and disease-related ligands.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014 May;140(5):689-99. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1587-5. Epub 2014 Jan 28. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24469254 Free PMC article.
-
Role of TNF-α-Inducing Protein Secreted by Helicobacter pylori as a Tumor Promoter in Gastric Cancer and Emerging Preventive Strategies.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Mar 1;13(3):181. doi: 10.3390/toxins13030181. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33804551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human gastric cancer development with TNF-α-inducing protein secreted from Helicobacter pylori.Cancer Lett. 2012 Sep 28;322(2):133-8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.03.027. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Cancer Lett. 2012. PMID: 22459353 Review.
Cited by
-
Crystal structure of TNF-α-inducing protein from Helicobacter pylori in active form reveals the intrinsic molecular flexibility for unique DNA-binding.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41871. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041871. Epub 2012 Jul 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22860022 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of TNFα-interacting protein α (Tipα)-associated gastric carcinogenesis by BTG2/TIS21 via downregulating cytoplasmic nucleolin expression.Exp Mol Med. 2018 Feb 23;50(2):e449. doi: 10.1038/emm.2017.281. Exp Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29472702 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo NCL targeting affects breast cancer aggressiveness through miRNA regulation.J Exp Med. 2013 May 6;210(5):951-68. doi: 10.1084/jem.20120950. Epub 2013 Apr 22. J Exp Med. 2013. PMID: 23610125 Free PMC article.
-
Cell surface expression of nucleolin mediates the antiangiogenic and antitumor activities of kallistatin.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 16;9(2):2220-2235. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23346. eCollection 2018 Jan 5. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29416766 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of host proteins by Helicobacter cysteine-rich protein C.Curr Microbiol. 2011 Sep;63(3):239-49. doi: 10.1007/s00284-011-9969-2. Epub 2011 Jul 7. Curr Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21735226
References
-
- Balkwill F (2009) Tumour necrosis factor and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 9:361–371 - PubMed
-
- Borer RA, Lehner CF, Eppenberger HM, Nigg EA (1989) Major nucleolar proteins shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm. Cell 56:379–390 - PubMed
-
- Carpentier M, Morelle W, Coddeville B, Pons A, Masson M, Mazurier J, Legrand D (2005) Nucleolin undergoes partial N- and O-glycosylations in the extranuclear cell compartment. Biochemistry 44:5804–5815 - PubMed
-
- El-Omar EM, Carrington M, Chow WH, McColl KE, Bream JH, Young HA, Herrera J, Lissowska J, Yuan CC, Rothman N, Lanyon G, Martin M, Fraumeni JF Jr, Rabkin CS (2000) Interleukin-1 polymorphisms associated with increased risk of gastric cancer. Nature 404:398–402 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

