RNAi-based therapeutics-current status, challenges and prospects
- PMID: 20049714
- PMCID: PMC3378126
- DOI: 10.1002/emmm.200900023
RNAi-based therapeutics-current status, challenges and prospects
Abstract
RNA interference (RNAi) is a collection of small RNA directed mechanisms that result in sequence specific inhibition of gene expression. The notion that RNAi could lead to a new class of therapeutics caught the attention of many investigators soon after its discovery. The field of applied RNAi therapeutics has moved very quickly from lab to bedside. The RNAi approach has been widely used for drug development and several phase I and II clinical trials are under way. However, there are still some concerns and challenges to overcome for therapeutic applications. These include the potential for off-target effects, triggering innate immune responses and most importantly obtaining specific delivery into the cytoplasm of target cells. This review focuses on the current status of RNAi-based therapeutics, the challenges it faces and how to overcome them.
Figures
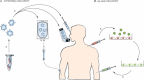
Systemic delivery: (a) double stranded siRNA is packaged into delivery vehicle (targeted nanoparticles, polymers, liposomes, etc.). (b) It is then given intravenously, via inhalator or direct injection into the target tissue (the eye, tumour, etc.).
ex-vivo delivery: (a) cells (dendritic cells, haematopoietic stem cells, etc.) are extracted from the patient and transduced with a virus containing shRNAs. (b) The genetically modified cells are then re-infused into the patient.
References
-
- Abdel-Wahab Z, Cisco R, Dannull J, Ueno T, Abdel-Wahab O, Kalady MF, Onaitis MW, Tyler DS, Pruitt SK. Cotransfection of DC with TLR4 and MART-1 RNA induces MART-1-specific responses. J Surg Res. 2005;124:264–273. - PubMed
-
- Anderson J, Li MJ, Palmer B, Remling L, Li S, Yam P, Yee JK, Rossi J, Zaia J, Akkina R. Safety and efficacy of a lentiviral vector containing three anti-HIV genes–CCR5 ribozyme, tat-rev siRNA, and TAR decoy–in SCID-hu mouse-derived T cells. Mol Ther. 2007;15:1182–1188. - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal R, Seth P, Willingham MC, Pastan I. pH-dependent lysis of liposomes by adenovirus. Biochemistry. 1986;25:2231–2237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

