Jamming bacterial communication: new approaches for the treatment of infectious diseases
- PMID: 20049722
- PMCID: PMC2801573
- DOI: 10.1002/emmm.200900032
Jamming bacterial communication: new approaches for the treatment of infectious diseases
Erratum in
- EMBO Mol Med. 2009 Sep;1(6-7):352-3
Abstract
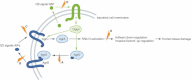
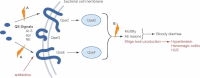
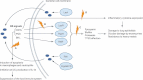
The global rise of anti-microbial resistance, combined with the rapid rate of microbial evolution, and the slower development of novel antibiotics, underscores the urgent need for innovative therapeutics. We are facing a post-antibiotic era with a decreased armamentarium to combat infectious diseases. Development of novel drugs will rely on basic research aimed to increase our understanding of bacterial pathogenesis and the inter-cellular chemical signalling among bacterial cells. Such basic science, when combined with contemporary drug discovery technologies, may be translated into therapeutic applications to combat bacterial infections. In this review, we discuss many strategies aimed to interfere with bacterial cell-to-cell signalling via the quorum-sensing (QS) pathway to inhibit bacterial virulence and/or the development of microbial communities (known as biofilms), which are refractory to antibiotic treatment. QS antagonists should be viewed as blockers of pathogenicity rather than as anti-microbials and because QS is not involved in bacterial growth, inhibition of QS should not yield a strong selective pressure for development of resistance. QS inhibitors (QSIs) hold great expectations and we look forward to their application in fighting bacterial infections.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Staphylococcus aureus; enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC); inter-kingdom signalling; quorum sensing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors: attractive alternatives for control of infectious pathogens showing multiple drug resistance.Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2013 Apr;8(1):68-83. doi: 10.2174/1574891x11308010012. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 23394143 Review.
-
Subinhibitory concentrations of phenyl lactic acid interfere with the expression of virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical strains.Roum Arch Microbiol Immunol. 2009 Jan-Mar;68(1):27-33. Roum Arch Microbiol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19507624
-
Quorum Sensing Inhibitors: An Alternative Strategy to Win the Battle against Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) Bacteria.Molecules. 2024 Jul 24;29(15):3466. doi: 10.3390/molecules29153466. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39124871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial and anti-Quorum Sensing activities of selected medicinal plants of Ethiopia: Implication for development of potent antimicrobial agents.BMC Microbiol. 2016 Jul 11;16(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12866-016-0765-9. BMC Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27400878 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of quorum sensing on microbial metabolism and human health.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2013;131:25-61. doi: 10.1007/10_2012_138. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 22767136 Review.
Cited by
-
The use of nanoscale visible light-responsive photocatalyst TiO2-Pt for the elimination of soil-borne pathogens.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31212. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031212. Epub 2012 Feb 22. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22384003 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of Appropriate Autoinducer Analogues for the Modulation of Quorum Sensing at the Host-Bacterium Interface.ACS Chem Biol. 2018 Nov 16;13(11):3115-3122. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.8b00676. Epub 2018 Oct 18. ACS Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 30296049 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Based Design and Biological Evaluation of Triphenyl Scaffold-Based Hybrid Compounds as Hydrolytically Stable Modulators of a LuxR-Type Quorum Sensing Receptor.ACS Infect Dis. 2016 Jan 8;2(1):32-38. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.5b00112. Epub 2015 Nov 2. ACS Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 26807436 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal Induces Oxidative Stress and Inhibits Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression in Lung Epithelial Cells.Infect Immun. 2017 Aug 18;85(9):e00176-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00176-17. Print 2017 Sep. Infect Immun. 2017. PMID: 28630072 Free PMC article.
-
Potent and Selective Modulation of the RhlR Quorum Sensing Receptor by Using Non-native Ligands: An Emerging Target for Virulence Control in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Chembiochem. 2015 Nov 2;16(16):2348-56. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201500357. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Chembiochem. 2015. PMID: 26460240 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balaban N, Goldkorn T, Gov Y, Hirshberg M, Koyfman N, Matthews HR, Nhan RT, Singh B, Uziel O. Regulation of Staphylococcus aureuspathogenesis via target of RNAIII-activating protein (TRAP) J Biol Chem. 2001;276:2658–2667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

