Jamming bacterial communication: new approaches for the treatment of infectious diseases
- PMID: 20049722
- PMCID: PMC2801573
- DOI: 10.1002/emmm.200900032
Jamming bacterial communication: new approaches for the treatment of infectious diseases
Erratum in
- EMBO Mol Med. 2009 Sep;1(6-7):352-3
Abstract
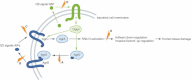
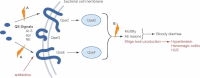
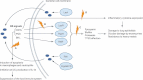
The global rise of anti-microbial resistance, combined with the rapid rate of microbial evolution, and the slower development of novel antibiotics, underscores the urgent need for innovative therapeutics. We are facing a post-antibiotic era with a decreased armamentarium to combat infectious diseases. Development of novel drugs will rely on basic research aimed to increase our understanding of bacterial pathogenesis and the inter-cellular chemical signalling among bacterial cells. Such basic science, when combined with contemporary drug discovery technologies, may be translated into therapeutic applications to combat bacterial infections. In this review, we discuss many strategies aimed to interfere with bacterial cell-to-cell signalling via the quorum-sensing (QS) pathway to inhibit bacterial virulence and/or the development of microbial communities (known as biofilms), which are refractory to antibiotic treatment. QS antagonists should be viewed as blockers of pathogenicity rather than as anti-microbials and because QS is not involved in bacterial growth, inhibition of QS should not yield a strong selective pressure for development of resistance. QS inhibitors (QSIs) hold great expectations and we look forward to their application in fighting bacterial infections.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Staphylococcus aureus; enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC); inter-kingdom signalling; quorum sensing.
Figures
References
-
- Balaban N, Goldkorn T, Gov Y, Hirshberg M, Koyfman N, Matthews HR, Nhan RT, Singh B, Uziel O. Regulation of Staphylococcus aureuspathogenesis via target of RNAIII-activating protein (TRAP) J Biol Chem. 2001;276:2658–2667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

