Top-down particle fabrication: control of size and shape for diagnostic imaging and drug delivery
- PMID: 20049805
- PMCID: PMC2804992
- DOI: 10.1002/wnan.40
Top-down particle fabrication: control of size and shape for diagnostic imaging and drug delivery
Abstract
This review discusses rational design of particles for use as therapeutic vectors and diagnostic imaging agent carriers. The emerging importance of both particle size and shape is considered, and the adaptation and modification of soft lithography methods to produce nanoparticles are highlighted. To this end, studies utilizing particles made via a process called Particle Replication In Non-wetting Templates are discussed. In addition, insights gained into therapeutic cargo and imaging agent delivery from related types of polymer-based carriers are considered.
(c) 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Figures




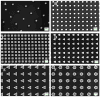
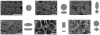



Similar articles
-
Engineering DNA scaffolds for delivery of anticancer therapeutics.Biomater Sci. 2015 Jul;3(7):1018-24. doi: 10.1039/c4bm00459k. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Biomater Sci. 2015. PMID: 26221936
-
Advantages of nanotechnology-based Chinese herb drugs on biological activities.Curr Drug Metab. 2009 Oct;10(8):905-13. doi: 10.2174/138920009790274603. Curr Drug Metab. 2009. PMID: 20214585 Review.
-
Nanoparticles and their applications in cell and molecular biology.Integr Biol (Camb). 2014 Jan;6(1):9-26. doi: 10.1039/c3ib40165k. Integr Biol (Camb). 2014. PMID: 24104563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Particle shape effects in vitro and in vivo.Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2012 Jun 1;4(4):1344-53. doi: 10.2741/s336. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2012. PMID: 22652876 Review.
-
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles improve magnetic labeling efficiency in human stem cells.Small. 2008 May;4(5):619-26. doi: 10.1002/smll.200700493. Small. 2008. PMID: 18491363
Cited by
-
Chemistry with spatial control using particles and streams().RSC Adv. 2012 Oct 28;2(26):9707-9726. doi: 10.1039/C2RA20337E. RSC Adv. 2012. PMID: 23145348 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the murine immune response to pulmonary delivery of precisely fabricated nano- and microscale particles.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 12;8(4):e62115. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062115. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23593509 Free PMC article.
-
Shaping cancer nanomedicine: the effect of particle shape on the in vivo journey of nanoparticles.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2014 Jan;9(1):121-34. doi: 10.2217/nnm.13.191. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2014. PMID: 24354814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Designer nanoparticles: incorporating size, shape and triggered release into nanoscale drug carriers.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2010 Apr;7(4):479-95. doi: 10.1517/17425240903579971. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2010. PMID: 20331355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of aspect ratio and deformability on nanoparticle extravasation through nanopores.Langmuir. 2012 Jun 12;28(23):8773-81. doi: 10.1021/la301279v. Epub 2012 May 29. Langmuir. 2012. PMID: 22612428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wong SY, Pelet JM, Putnam D. Polymer Systems for Gene Delivery - Past, Present, and Future. Prog Polym Sci. 2007;32:799–837.
-
- Zamboni WC. Concept and Clinical Evaluation of Carrier-Mediated Anticancer Agents. The Oncologist. 2008;13:248–260. - PubMed
-
- Nie S, Xing Y, Kim GJ, Simons JW. Nanotechnology: Applications in Cancer. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2007;9:257–288. - PubMed
-
- Cuchelkar V, Kopeček J. Polymer-Drug Conjugates. In: Uchegbu IF, Schaetzlain AG, editors. Polymers in Drug Delivery. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press LLC; 2006. pp. 155–182.
-
- Duncan R. The Dawning Era of Polymer Therapeutics. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2003;2:347–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

