Nanoparticles in sentinel lymph node mapping
- PMID: 20049820
- PMCID: PMC6309687
- DOI: 10.1002/wnan.48
Nanoparticles in sentinel lymph node mapping
Abstract
The lymph nodes and lymphatic vessels are more difficult to access than most vascular structures. Interstitial injection of imaging agents is often necessary to opacify the lymphatics. Traditionally, radionuclide methods of sentinel node imaging have dominated this field, however, limitations in resolution and exposure to radiation have encouraged the development of newer imaging methods. Among these are magnetic resonance lymphography in which a Gadolinium labeled nanoparticle is injected and imaged providing superior anatomic resolution and assessment of lymphatic dynamics. Optical imaging employing various nanoparticles including quantum dots also provide the capability of mapping each lymphatic basin in another "color". Taken together this "toolbox" of lymphatic imaging agents is poised to improve our understanding of the lymphatic system.
Copyright (c) 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Figures

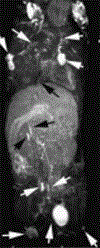
Similar articles
-
A dual-modal magnetic nanoparticle probe for preoperative and intraoperative mapping of sentinel lymph nodes by magnetic resonance and near infrared fluorescence imaging.J Biomater Appl. 2013 Jul;28(1):100-11. doi: 10.1177/0885328212437883. J Biomater Appl. 2013. PMID: 23812946 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic nanocarriers for sentinel lymph node imaging.J Control Release. 2009 Sep 1;138(2):90-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.05.010. Epub 2009 May 13. J Control Release. 2009. PMID: 19445982 Review.
-
Two-color lymphatic mapping using Ig-conjugated near infrared optical probes.J Invest Dermatol. 2007 Oct;127(10):2351-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700892. Epub 2007 May 24. J Invest Dermatol. 2007. PMID: 17522707
-
Dynamic imaging of lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes using a bimodal nanoparticulate contrast agent.Lymphat Res Biol. 2007;5(3):151-8. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2007.5302. Lymphat Res Biol. 2007. PMID: 18035933
-
Anatomy and physiology of lymphatic drainage of the breast from the perspective of sentinel node biopsy.J Am Coll Surg. 2001 Mar;192(3):399-409. doi: 10.1016/s1072-7515(00)00776-6. J Am Coll Surg. 2001. PMID: 11245383 Review.
Cited by
-
Intrinsically germanium-69-labeled iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and in-vivo dual-modality PET/MR imaging.Adv Mater. 2014 Aug 13;26(30):5119-23. doi: 10.1002/adma.201401372. Epub 2014 Jun 18. Adv Mater. 2014. PMID: 24944166 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress on semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for molecular imaging and cancer phototherapy.Biomaterials. 2018 Feb;155:217-235. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.11.025. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Biomaterials. 2018. PMID: 29190479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design and Synthesis of 99mTcN-Labeled Dextran-Mannose Derivatives for Sentinel Lymph Node Detection.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018 Jul 16;11(3):70. doi: 10.3390/ph11030070. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30012952 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional MRI/PET Nanobeacons Derived from the in Situ Self-Assembly of Translational Polymers and Clinical Cargo through Coalescent Intermolecular Forces.Nano Lett. 2015 Dec 9;15(12):8032-43. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b03370. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Nano Lett. 2015. PMID: 26540670 Free PMC article.
-
Rational chemical design of the next generation of molecular imaging probes based on physics and biology: mixing modalities, colors and signals.Chem Soc Rev. 2011 Sep;40(9):4626-48. doi: 10.1039/c1cs15077d. Epub 2011 May 23. Chem Soc Rev. 2011. PMID: 21607237 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moghimi SM, Hunter AC, Murray JC. Nanomedicine: current status and future prospects. Faseb J 2005, 19(3):311–330. - PubMed
-
- Krag D, Weaver D, Ashikaga T, Moffat F, Klimberg VS, et al. The sentinel node in breast cancer-a multicenter validation study. N Engl J Med 1998, 339(14):941–946. - PubMed
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group(EBCTCG). Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 2005, 365(9472):1687–1717. - PubMed
-
- Morton DL, Wen DR, Wong JH, Economou JS, Cagle LA, et al. Technical details of intraoperative lymphatic mapping for early stage melanoma. Arch Surg 1992, 127(4):392–399. - PubMed
-
- Cabanas RM. An approach for the treatment of penile carcinoma. Cancer 1977, 39(2):456–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

