Peripheral blood stem cell support for multiple cycles of dose intensive induction therapy is feasible with little risk of tumor contamination in advanced stage neuroblastoma: a report from the Childrens Oncology Group
- PMID: 20049927
- PMCID: PMC2905158
- DOI: 10.1002/pbc.22344
Peripheral blood stem cell support for multiple cycles of dose intensive induction therapy is feasible with little risk of tumor contamination in advanced stage neuroblastoma: a report from the Childrens Oncology Group
Abstract
Background: Poor outcome in Stage 4 neuroblastoma may be improved with increased dose intensity of therapy. We investigated the feasibility of sequential collection and infusion of peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCs) as hematopoietic support for non-myeloablative dose intensive induction chemotherapy given every 21-28 days.
Methods: Twenty-two children with Stage 4 neuroblastoma (>or=1 year of age) received two cycles of high-dose cyclophosphamide (4 g/m(2)), doxorubicin (75 mg/m(2)), and vincristine (2 mg/m(2)) followed by three cycles of interpatient dose escalating carboplatin (Dose Level 0 = 800 mg/m(2); Dose Level 1 = 1,000 mg/m(2)), high-dose cyclophosphamide (4 g/m(2)), and etoposide (600 mg/m(2)). PBSC were harvested following cycle 2, 3, and 4 in Cohort 1 and infused after each subsequent cycle. In Cohort 2, PBSC were harvested after cycle 2 and split into three aliquots for infusion. Dose limiting toxicity (DLT) and ability to administer cycles within 28 days was assessed.
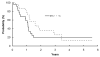
Results: Sufficient PBSC (>or=2 x 10(6) CD34 cells/kg per infusion) were collected from 17/21 eligible patients with minimal toxicity and no detectable neuroblastoma cells by immunocytology. Carboplatin at 1000 mg/m(2) resulted in DLT of delayed platelet recovery >28 days in 4/8 patients. Despite de-escalation to 800 mg/m(2), platelet DLT occurred in 4/7 Cohort 1 and 3/7 Cohort 2 patients.
Conclusion: As defined in this protocol, doses of carboplatin were not tolerable with the PBSC dose administered. However, it was feasible to collect sufficient PBSC from small neuroblastoma patients to use as hematopoietic support with minimal risk of tumor contamination and toxicity.
Keywords: carboplatin; dose intensity; neuroblastoma; peripheral blood stem cell support.
Figures
References
-
- Matthay KK, Villablanca JG, Seeger RC, et al. Treatment of high-risk neuroblastoma with intensive chemotherapy, radiotherapy, autologous bone marrow transplantation, and 13-cis-retinoic acid. Children’s Cancer Group. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(16):1165–73. - PubMed
-
- Frappaz D, Michon J, Coze C, et al. LMCE3 treatment strategy: Results in 99 consecutively diagnosed stage 4 neuroblastomas in children older than 1 year at diagnosis. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:468–476. - PubMed
-
- Matthay K, Atkinson J, Stram DO, et al. Patterns of relapse after autologous purged bone marrow transplantation for neuroblastoma: a Children’s Cancer Group pilot study. J Clin Oncol. 1993;11:2226–2233. - PubMed
-
- Cheung NK, Heller G. Chemotherapy dose intensity correlates strongly with response, median survival and median progression-free survival in metastatic neuroblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 1991;9:1050–1058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials