Multiple muscarinic pathways mediate the suppression of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in mouse intestinal smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 20050185
- PMCID: PMC2807649
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00475.x
Multiple muscarinic pathways mediate the suppression of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in mouse intestinal smooth muscle cells
Abstract
Background and purpose: Stimulation of muscarinic receptors in intestinal smooth muscle cells results in suppression of voltage-gated Ca2+ channel currents (I(Ca)). However, little is known about which receptor subtype(s) mediate this effect.
Experimental approach: The effect of carbachol on I(Ca) was studied in single intestinal myocytes from M2 or M3 muscarinic receptor knockout (KO) and wild-type (WT) mice.
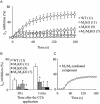
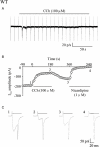
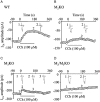
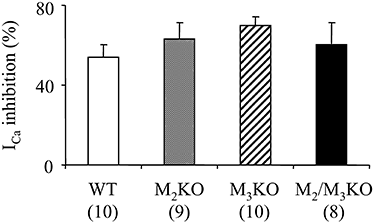
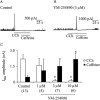
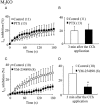
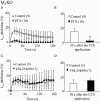
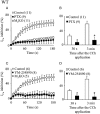
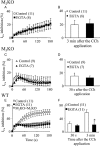
Key results: In M2KO cells, carbachol (100 microM) induced a sustained I(Ca) suppression as seen in WT cells. However, this suppression was significantly smaller than that seen in WT cells. Carbachol also suppressed I(Ca) in M3KO cells, but with a phasic time course. In M2/M3-double KO cells, carbachol had no effect on I(Ca). The extent of the suppression in WT cells was greater than the sum of the I(Ca) suppressions in M2KO and M3KO cells, indicating that it is not a simple mixture of M2 and M3 receptor responses. The G(i/o) inhibitor, Pertussis toxin, abolished the I(Ca) suppression in M3KO cells, but not in M2KO cells. In contrast, the G(q/11) inhibitor YM-254890 strongly inhibited only the I(Ca) suppression in M2KO cells. Suppression of I(Ca) in WT cells was markedly reduced by either Pertussis toxin or YM-254890.
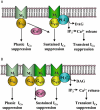
Conclusion and implications: In intestinal myocytes, M2 receptors mediate a phasic I(Ca) suppression via G(i/o) proteins, while M3 receptors mediate a sustained I(Ca) suppression via G(q/11) proteins. In addition, another pathway that requires both M2/G(i/o) and M3/G(q/11) systems may be operative in inducing a sustained I(Ca) suppression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Muscarinic receptor subtypes involved in carbachol-induced contraction of mouse uterine smooth muscle.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008 Jun;377(4-6):503-13. doi: 10.1007/s00210-007-0223-1. Epub 2007 Dec 11. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18071676
-
Three distinct muscarinic signalling pathways for cationic channel activation in mouse gut smooth muscle cells.J Physiol. 2007 Jul 1;582(Pt 1):41-61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.133165. Epub 2007 Apr 26. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17463038 Free PMC article.
-
Muscarinic suppression of ATP-sensitive K+ channels mediated by the M3/Gq/11/phospholipase C pathway contributes to mouse ileal smooth muscle contractions.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018 Oct 1;315(4):G618-G630. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00069.2018. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30001145
-
Nonselective cation channels activated by the stimulation of muscarinic receptors in mammalian gastric smooth muscle.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2003 Dec;39(6):231-47. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.39.231. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2003. PMID: 15048016 Review.
-
Functions of Muscarinic Receptor Subtypes in Gastrointestinal Smooth Muscle: A Review of Studies with Receptor-Knockout Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 18;22(2):926. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020926. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33477687 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of transient receptor potential melastatin 4 channels in the resting membrane potential setting and cholinergic contractile responses in mouse detrusor and ileal smooth muscles.J Vet Med Sci. 2019 Feb 19;81(2):217-228. doi: 10.1292/jvms.18-0631. Epub 2018 Dec 6. J Vet Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30518701 Free PMC article.
-
Possible antagonistic effects of the TRPC4 channel blocker ML204 on M2 and M3 muscarinic receptors in mouse ileal and detrusor smooth muscles and atrial myocardium.J Vet Med Sci. 2018 Sep 13;80(9):1407-1415. doi: 10.1292/jvms.18-0197. Epub 2018 Jul 5. J Vet Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 29973432 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin acutely lowers blood glucose levels by inhibition of intestinal glucose transport.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 16;9(1):6156. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42531-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30992489 Free PMC article.
-
Key features of the genetic architecture and evolution of host-microbe interactions revealed by high-resolution genetic mapping of the mucosa-associated gut microbiome in hybrid mice.Elife. 2022 Jul 19;11:e75419. doi: 10.7554/eLife.75419. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35866635 Free PMC article.
-
Type 3 muscarinic receptors contribute to intestinal mucosal homeostasis and clearance of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis through induction of TH2 cytokines.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016 Jul 1;311(1):G130-41. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00461.2014. Epub 2016 May 12. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27173511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dustin P. General physiology of tubulins and microtubules. In: Dustin P, editor. Microtubules. New York: Springer-Verlag; 1984. pp. 94–126.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

