Novel effects mediated by bradykinin and pharmacological characterization of bradykinin B2 receptor antagonism in human synovial fibroblasts
- PMID: 20050188
- PMCID: PMC2807661
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00511.x
Novel effects mediated by bradykinin and pharmacological characterization of bradykinin B2 receptor antagonism in human synovial fibroblasts
Abstract
Background and purpose: Bradykinin (BK) and B2 receptors have been implicated in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis (OA), and synovitis is one of its hallmarks. Here, the selective B2 receptor antagonists MEN16132 and icatibant have been pharmacologically characterized in human synovial cells.
Experimental approach: Radioligand and functional studies (inositol phosphate (IP) accumulation, interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 release) were performed in cultured synoviocytes.
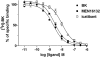
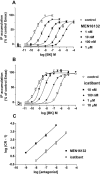
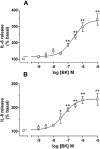
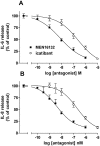
Key results: [3H]-BK saturation studies indicated receptor density (Bmax) and K(d) values of 121,550 sites per cell and 1.14 nM respectively. In synoviocytes, MEN16132 (pK(I) 8.9) was threefold more potent than icatibant (pK(I) 8.4). Both antagonists showed competitive antagonism in the BK-induced IP assay (control EC50 0.45 nM), with pK(B) values of 9.9 (MEN16132) and 8.1 (icatibant). 24h incubation with BK induced IL-6 (EC50 216 nM) and IL-8 (EC50 53 nM) release. Both MEN16132 (IL-6: pIC50 8.1; IL-8: pIC50 8.4) and icatibant (IL-6: pIC50 6.6; IL-8: pIC50 6.7) completely prevented this BK-induced release. Indomethacin did not affect the basal or the IL-6/IL-8 release induced by BK, whereas nordihydroguaiaretic acid decreased the basal release, although BK still increased IL-6 and IL-8 production. BK-induced IL-8 release was attenuated by inhibitors of phospholipase C (U73122), p38 (SB203580), JNK (SP600125), ERK 1/2 (PD98059) MAPKs, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (LY294002), NF-kappaB (BAY-117085) and by the glucocorticoid dexamethasone.
Conclusions and implications: Bradykinin via B2 receptors can participate in inflammatory events in synovitis. MEN16132 is a highly potent B2 receptor antagonist capable of blocking pro-inflammatory responses to BK evoked in human synoviocytes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fasitibant prevents the bradykinin and interleukin 1β synergism on prostaglandin E₂ release and cyclooxygenase 2 expression in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2012 Aug;385(8):777-86. doi: 10.1007/s00210-012-0762-y. Epub 2012 May 26. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22638761
-
Bradykinin and B₂ receptor antagonism in rat and human articular chondrocytes.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Feb;162(3):611-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01062.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20946124 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the molecular interactions of two antagonists, MEN16132 or icatibant, at the human kinin B₂ receptor.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Mar;162(5):1202-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01133.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21108627 Free PMC article.
-
MEN16132, a novel potent and selective nonpeptide antagonist for the human bradykinin B2 receptor. In vitro pharmacology and molecular characterization.Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Dec 28;528(1-3):7-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.10.014. Epub 2005 Dec 1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16324696
-
Knee osteoarthritis: a role for bradykinin?Inflamm Res. 2008 Aug;57(8):351-61. doi: 10.1007/s00011-007-7204-1. Inflamm Res. 2008. PMID: 18787773 Review.
Cited by
-
G protein-coupled receptors in rheumatology.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014 Jul;10(7):429-36. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2014.62. Epub 2014 May 6. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24798574 Review.
-
Fasitibant prevents the bradykinin and interleukin 1β synergism on prostaglandin E₂ release and cyclooxygenase 2 expression in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2012 Aug;385(8):777-86. doi: 10.1007/s00210-012-0762-y. Epub 2012 May 26. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22638761
-
The emerging role of fibroblast-like synoviocytes-mediated synovitis in osteoarthritis: An update.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Sep;24(17):9518-9532. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15669. Epub 2020 Jul 19. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32686306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antagonism of bradykinin B2 receptor prevents inflammatory responses in human endothelial cells by quenching the NF-kB pathway activation.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 2;9(1):e84358. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084358. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24392129 Free PMC article.
-
Bradykinin and B₂ receptor antagonism in rat and human articular chondrocytes.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Feb;162(3):611-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01062.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20946124 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bathon JM, Manning DC, Goldman DW, Towns MC, Proud D. Characterization of kinin receptors on human synovial cells and upregulation of receptor number by interleukin-1. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992a;260:384–392. - PubMed
-
- Bathon JM, Croghan JC, MacGlashan DW, Jr, Proud D. Bradykinin is a potent and relatively selective stimulus for cytosolic calcium elevation in human synovial cells. J Immunol. 1994;153:2600–2608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

