Divergence of biochemical function in the HAD superfamily: D-glycero-D-manno-heptose-1,7-bisphosphate phosphatase (GmhB)
- PMID: 20050615
- PMCID: PMC2844805
- DOI: 10.1021/bi902018y
Divergence of biochemical function in the HAD superfamily: D-glycero-D-manno-heptose-1,7-bisphosphate phosphatase (GmhB)
Abstract
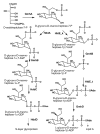
D-Glycero-d-manno-heptose-1,7-bisphosphate phosphatase (GmhB) is a member of the histidinol-phosphate phosphatase (HisB) subfamily of the haloalkanoic acid dehalogenase (HAD) enzyme superfamily. GmhB supports two divergent biochemical pathways in bacteria: the d-glycero-d-manno-heptose-1alpha-GDP pathway (in S-layer glycoprotein biosynthesis) and the l-glycero-d-manno-heptose-1beta-ADP pathway (in lipid A biosynthesis). Herein, we report the comparative analysis of substrate recognition in selected GmhB orthologs. The substrate specificity of the l-glycero-d-manno-heptose-1beta-ADP pathway GmhB from Escherichia coli K-12 was evaluated using hexose and heptose bisphosphates, histidinol phosphate, and common organophosphate metabolites. Only d-glycero-d-manno-heptose 1beta,7-bisphosphate (k(cat)/K(m) = 7 x 10(6) M(-1) s(-1)) and d-glycero-d-manno-heptose 1alpha,7-bisphosphate (k(cat)/K(m) = 7 x 10(4) M(-1) s(-1)) displayed physiologically significant substrate activity. (31)P NMR analysis demonstrated that E. coli GmhB selectively removes the C(7) phosphate. Steady-state kinetic inhibition studies showed that d-glycero-d-manno-heptose 1beta-phosphate (K(is) = 60 microM, and K(ii) = 150 microM) and histidinol phosphate (K(is) = 1 mM, and K(ii) = 6 mM), while not hydrolyzed, do in fact bind to E. coli GmhB, which leads to the conclusion that nonproductive binding contributes to substrate discrimination. High catalytic efficiency and a narrow substrate range are characteristic of a well-evolved metabolic enzyme, and as such, E. coli GmhB is set apart from most HAD phosphatases (which are typically inefficient and promiscuous). The specialization of the biochemical function of GmhB was examined by measuring the kinetic constants for hydrolysis of the alpha- and beta-anomers of d-glycero-d-manno-heptose 1beta,7-bisphosphate catalyzed by the GmhB orthologs of the l-glycero-d-manno-heptose 1beta-ADP pathways operative in Bordetella bronchiseptica and Mesorhizobium loti and by the GmhB of the d-glycero-d-manno-heptose 1alpha-GDP pathway operative in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. The results show that although each of these representatives possesses physiologically significant catalytic activity toward both anomers, each displays substantial anomeric specificity. Like E. coli GmhB, B. bronchiseptica GmhB and M. loti GmhB prefer the beta-anomer, whereas B. thetaiotaomicron GmhB is selective for the alpha-anomer. By determining the anomeric configuration of the physiological substrate (d-glycero-d-manno-heptose 1,7-bisphosphate) for each of the four GmhB orthologs, we discovered that the anomeric specificity of GmhB correlates with that of the pathway kinase. The conclusion drawn from this finding is that the evolution of the ancestor to GmhB in the HisB subfamily provided for specialization toward two distinct biochemical functions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Experimental and computational analysis of the ancestry of an evolutionary young enzyme from histidine biosynthesis.Protein Sci. 2023 Jan;32(1):e4536. doi: 10.1002/pro.4536. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 36502290 Free PMC article.
-
Structural determinants of substrate recognition in the HAD superfamily member D-glycero-D-manno-heptose-1,7-bisphosphate phosphatase (GmhB).Biochemistry. 2010 Feb 16;49(6):1082-92. doi: 10.1021/bi902019q. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20050614 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis of nucleotide-activated D-glycero-D-manno-heptose.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jun 15;276(24):20935-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100378200. Epub 2001 Mar 28. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11279237
-
ADP-heptose: A new innate immune modulator.Carbohydr Res. 2019 Feb 1;473:123-128. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2018.12.011. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Carbohydr Res. 2019. PMID: 30684847 Review.
-
Markers of fitness in a successful enzyme superfamily.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2009 Dec;19(6):658-65. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2009.09.008. Epub 2009 Nov 2. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2009. PMID: 19889535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Experimental and computational analysis of the ancestry of an evolutionary young enzyme from histidine biosynthesis.Protein Sci. 2023 Jan;32(1):e4536. doi: 10.1002/pro.4536. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 36502290 Free PMC article.
-
Improving microbial fitness in the mammalian gut by in vivo temporal functional metagenomics.Mol Syst Biol. 2015 Mar;11(3):788. doi: 10.15252/msb.20145866. Mol Syst Biol. 2015. PMID: 26148351 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori GmhB enzyme involved in ADP-heptose biosynthesis pathway is essential for lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis and bacterial virulence.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):1610-1628. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1938449. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 34125649 Free PMC article.
-
d-Sedoheptulose-7-phosphate is a common precursor for the heptoses of septacidin and hygromycin B.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Mar 13;115(11):2818-2823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1711665115. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29483275 Free PMC article.
-
Panoramic view of a superfamily of phosphatases through substrate profiling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 21;112(16):E1974-83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1423570112. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25848029 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Koonin EV, Tatusov RL. Computer Analysis of Bacterial Haloacid Dehalogenases Defines a Large Superfamily of Hydrolases with Diverse Specificity: Application of an Iterative Approach to Database Search. Journal of Molecular Biology. 1994;244:125–132. - PubMed
-
- Burroughs AM, Allen KN, Dunaway-Mariano D, Aravind L. Evolutionary genomics of the HAD superfamily: understanding the structural adaptations and catalytic diversity in a superfamily of phosphoesterases and allied enzymes. J Mol Biol. 2006;361:1003–1034. - PubMed
-
- Kneidinger B, Graninger M, Puchberger M, Kosma P, Messner P. Biosynthesis of nucleotide-activated D-glycero-D-manno-heptose. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:20935–20944. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

