Protein (19)F NMR in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 20050707
- PMCID: PMC2815348
- DOI: 10.1021/ja907966n
Protein (19)F NMR in Escherichia coli
Abstract
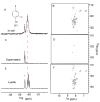
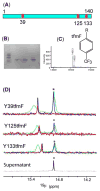
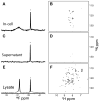
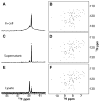
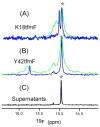
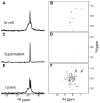
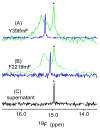
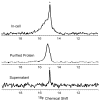
Although overexpression and (15)N enrichment facilitate the observation of resonances from disordered proteins in Escherichia coli, (15)N enrichment alone is insufficient for detecting most globular proteins. Here, we explain this dichotomy and overcome the problem while extending the capability of in-cell NMR by using (19)F-labeled proteins. Resonances from small (approximately 10 kDa) globular proteins containing the amino acid analogue 3-fluoro-tyrosine can be observed in cells, but for larger proteins the (19)F resonances are broadened beyond detection. Incorporating the amino acid analogue trifluoromethyl-L-phenylalanine allows larger proteins (up to 100 kDa) to be observed in cells. We also show that site-specific structural and dynamic information about both globular and disordered proteins can be obtained inside cells by using (19)F NMR.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

