Comparison of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound and pulsed electromagnetic field treatments on OPG and RANKL expression in human osteoblast-like cells
- PMID: 20050743
- PMCID: PMC8985733
- DOI: 10.2319/060809-318.1
Comparison of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound and pulsed electromagnetic field treatments on OPG and RANKL expression in human osteoblast-like cells
Abstract
Objective: To compare two clinically applied treatments to stimulate bone healing-low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) and pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF)-for their effects on RANKL and OPG expression in osteoblast-like cells in vitro.
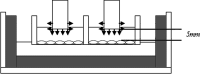
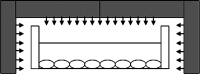
Materials and methods: LIPUS or PEMF was applied to Saos-2 cells for 10 minutes or 3 hours. RANKL and OPG expressions were analyzed at 0, 4, 8, or 12 hours after treatment with real-time PCR. Secreted protein levels in culture supernatant were analyzed at the same posttreatment time points using specific ELISA assays.
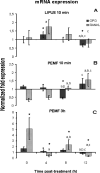
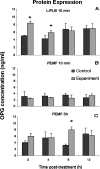
Results: Neither LIPUS nor PEMF had an effect on RANKL protein expression. OPG protein was significantly increased by LIPUS after 0 and 4 hours (brief short-term effect) and was increased almost 2.5-fold by PEMF after 8 hours. The mRNA levels of OPG and RANKL were hardly affected by LIPUS treatment at any time point. PEMF induced a fivefold increase in RANKL mRNA expression at t = 0. A brief PEMF treatment of 10 minutes resulted in downregulation of RANKL expression after 0 and 4 hours and upregulation at 12 hours. OPG mRNA was downregulated after 8 hours.
Conclusion: The effects of LIPUS or PEMF expression on OPG and RANKL are limited. From our experiments, it seems that LIPUS treatment resulted in a quick protein response, while the response of cells to PEMF (3 hours) was delayed. The increase in OPG protein at 8 hours post PEMF treatment is indicative of reduction of osteolysis.
Figures
References
-
- Fredericks D. C, Nepola J. V, Baker J. T, Abbott J, Simon B. Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on bone healing in a rabbit tibial osteotomy model. J Orthop Trauma. 2000;14:93–100. - PubMed
-
- Duarte L. R. The stimulation of bone growth by ultrasound. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1983;101:153–159. - PubMed
-
- Claes L, Willie B. The enhancement of bone regeneration by ultrasound. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2007;93:384–398. - PubMed
-
- Khosla S. Minireview: the OPG/RANKL/RANK system. Endocrinology. 2001;142:5050–5055. - PubMed
-
- Boyce B. F, Xing L. The RANKL/RANK/OPG pathway. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2007;5:98–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

