Leptin levels in gingival crevicular fluid during orthodontic tooth movement
- PMID: 20050744
- PMCID: PMC8985734
- DOI: 10.2319/072109-402.1
Leptin levels in gingival crevicular fluid during orthodontic tooth movement
Abstract
Objectives: To test if leptin can be detected in the gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) around moving teeth, and to determine whether any changes occur during orthodontic tooth movement.
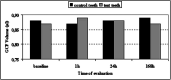
Materials and methods: An upper canine requiring distal movement served as the test tooth; the contralateral canine was used as a control tooth. The control tooth was included in the orthodontic appliance, but was not subjected to the orthodontic force. GCF sampling from the distal sites of the test and control teeth was done at baseline, 1 hour, 24 hours, and 168 hours.
Results: Leptin concentrations of the test teeth decreased in a time-dependent manner. When compared with the baseline measurement, the decrease was significant at 168 hours (P < .05).
Conclusions: The concentration of leptin in GCF is decreased by orthodontic tooth movement; the results of the present study also suggest that leptin may have been one of the mediators responsible for orthodontic tooth movement.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The monitoring of gingival crevicular fluid volume during orthodontic treatment: a longitudinal randomized split-mouth study.Eur J Orthod. 2012 Feb;34(1):109-13. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjq172. Epub 2011 Jan 27. Eur J Orthod. 2012. PMID: 21273285 Clinical Trial.
-
Alkaline phosphatase activity in gingival crevicular fluid during human orthodontic tooth movement.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002 Nov;122(5):548-56. doi: 10.1067/mod.2002.126154. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002. PMID: 12439484
-
Lactate dehydrogenase activity in human gingival crevicular fluid during orthodontic treatment: a controlled, short-term longitudinal study.J Periodontol. 2005 Mar;76(3):411-7. doi: 10.1902/jop.2005.76.3.411. J Periodontol. 2005. PMID: 15857076 Clinical Trial.
-
Challenges and Perspectives Regarding the Determination of Gingival Crevicular Fluid Biomarkers During Orthodontic Treatment: A Narrative Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Dec 4;60(12):2004. doi: 10.3390/medicina60122004. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39768884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated bioinformatic analysis of protein landscape in gingival crevicular fluid unveils sequential bioprocess in orthodontic tooth movement.Prog Orthod. 2024 Sep 23;25(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s40510-024-00536-0. Prog Orthod. 2024. PMID: 39307846 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A cross-sectional cohort study of gingival crevicular fluid biomarkers in normal-weight and obese subjects during orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances.Angle Orthod. 2019 Nov;89(6):930-935. doi: 10.2319/100518-719.1. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Angle Orthod. 2019. PMID: 30920872 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Leptin on Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts during Mechanical Strain.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 25;22(13):6847. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136847. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34202165 Free PMC article.
-
Tooth movement, orofacial pain, and leptin, interleukin-1β, and tumor necrosis factor-α levels in obese adolescents.Angle Orthod. 2022 Jan 1;92(1):95-100. doi: 10.2319/011321-44.1. Angle Orthod. 2022. PMID: 34338736 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin Levels in Gingival Crevicular Fluid during Orthodontic Tooth Movement.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2021 Nov;13(Suppl 2):S1174-S1177. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_285_21. Epub 2021 Nov 10. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2021. PMID: 35017951 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Salivary Leptin Levels in Healthy Subjects and Patients with Advanced Periodontitis.J Dent (Tehran). 2016 Jan;13(1):1-9. J Dent (Tehran). 2016. PMID: 27536322 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nishijima Y, Yamaguchi M, Kojima T, Aihara N, Nakajima R, Kasai K. Levels of RANKL and OPG in gingival crevicular fluid during orthodontic tooth movement and effect of compression force on releases from periodontal ligament cells in vitro. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2006;9:63–70. - PubMed
-
- Davidovitch Z, Nicolay O. F, Ngan P. W, Shanfeld J. L. Neurotransmitters, cytokines, and the control of alveolar bone remodeling in orthodontics. Dent Clin North Am. 1988;32:411–435. - PubMed
-
- Uematsu S, Mogi M, Deguchi T. Interleukin (IL)-1 beta, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, epidermal growth factor, and beta 2-microglobulin levels are elevated in gingival crevicular fluid during human orthodontic tooth movement. J Dent Res. 1996;75:562–567. - PubMed
-
- Perinetti G, Paolantonio M, D'Attilio M, et al. Alkaline phosphatase activity in gingival crevicular fluid during human orthodontic tooth movement. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002;122:548–556. - PubMed
-
- Griffiths G. S, Moulson A. M, Petrie A, James I. T. Evaluation of osteocalcin and pyridinium crosslinks of bone collagen as markers of bone turnover in gingival crevicular fluid during different stages of orthodontic treatment. J Clin Periodontol. 1998;25:492–498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical