P2Y receptors and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- PMID: 20050854
- PMCID: PMC2825354
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00497.x
P2Y receptors and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
Abstract
Background and purpose: P2Y nucleotide receptors are involved in the regulation of vascular tone, smooth muscle cell (SMC) proliferation and inflammatory responses. The present study investigated whether they are involved in atherosclerosis.
Experimental approach: mRNA of P2Y receptors was quantified (RT-PCR) in atherosclerotic and plaque-free aorta segments of apolipoprotein E-deficient (apoE(-/-)) mice. Macrophage activation was assessed in J774 macrophages, and effects of non-selective purinoceptor antagonists on atherosclerosis were evaluated in cholesterol-fed apoE(-/-) mice.
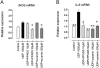
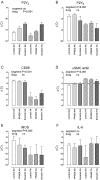
Key results: P2Y(6) receptor mRNA was consistently elevated in segments with atherosclerosis, whereas P2Y(2) receptor expression remained unchanged. Expression of P2Y(1) or P2Y(4) receptor mRNA was low or undetectable, and not influenced by atherosclerosis. P2Y(6) mRNA expression was higher in cultured J774 macrophages than in cultured aortic SMCs. Furthermore, immunohistochemical staining of plaques demonstrated P2Y(6)-positive macrophages, but few SMCs, suggesting that macrophage recruitment accounted for the increase in P2Y(6) receptor mRNA during atherosclerosis. In contrast to ATP, the P2Y(6)-selective agonist UDP increased mRNA expression and activity of inducible nitric oxide synthase and interleukin-6 in J774 macrophages; this effect was blocked by suramin (100-300 microM) or pyridoxal-phosphate-6-azophenyl-2'-4'-disulphonic acid (PPADS, 10-30 microM). Finally, 4-week treatment of cholesterol-fed apoE(-/-) mice with suramin or PPADS (50 and 25 mg.kg(-1).day(-1) respectively) reduced plaque size, without changing plaque composition (relative SMC and macrophage content) or cell replication.
Conclusions and implications: These results suggest involvement of nucleotide receptors, particularly P2Y(6) receptors, during atherosclerosis, and warrant further research with selective purinoceptor antagonists or P2Y(6) receptor-deficient mice.
Figures


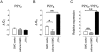



Similar articles
-
Endothelial Cell-Specific Deletion of P2Y2 Receptor Promotes Plaque Stability in Atherosclerosis-Susceptible ApoE-Null Mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Jan;37(1):75-83. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308561. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 27856454 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced atherosclerotic lesions in P2Y1/apolipoprotein E double-knockout mice: the contribution of non-hematopoietic-derived P2Y1 receptors.Circulation. 2008 Aug 12;118(7):754-63. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.788927. Epub 2008 Jul 28. Circulation. 2008. PMID: 18663083
-
Evidence that rat hepatocytes co-express functional P2Y1 and P2Y2 receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Feb;129(4):764-70. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703103. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10683201 Free PMC article.
-
Design and pharmacology of selective P2-purinoceptor antagonists.J Auton Pharmacol. 1996 Dec;16(6):341-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1996.tb00049.x. J Auton Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 9131412 Review.
-
International Union of Pharmacology LVIII: update on the P2Y G protein-coupled nucleotide receptors: from molecular mechanisms and pathophysiology to therapy.Pharmacol Rev. 2006 Sep;58(3):281-341. doi: 10.1124/pr.58.3.3. Pharmacol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16968944 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pyrimidine Nucleotides Containing a (S)-Methanocarba Ring as P2Y6 Receptor Agonists.Medchemcomm. 2017 Oct 1;8(10):1897-1908. doi: 10.1039/C7MD00397H. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Medchemcomm. 2017. PMID: 29423136 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of HIV-mediated blood-brain barrier compromise and leukocyte transmigration under the current antiretroviral era.iScience. 2024 Feb 15;27(3):109236. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109236. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38487019 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of glucose uptake in mouse skeletal muscle cells and adipocytes by P2Y6 receptor agonists.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 30;9(12):e116203. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116203. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25549240 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of an inhibitor of DNA-driven inflammation that preferentially targets the AIM2 inflammasome.iScience. 2023 Apr 27;26(5):106758. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106758. eCollection 2023 May 19. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37216118 Free PMC article.
-
The role of nucleotides and purinergic signaling in apoptotic cell clearance - implications for chronic inflammatory diseases.Front Immunol. 2014 Dec 23;5:656. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00656. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25566266 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bar I, Guns PJ, Metallo J, Cammarata D, Wilkin F, Boeynaems JM, et al. Knock-out mice reveal a role for P2Y6 receptor in macrophages, endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2008;74:777–784. - PubMed
-
- Cox MA, Gomes B, Palmer K, Du K, Wiekowski M, Wilburn B, et al. The pyrimidinergic P2Y6 receptor mediates a novel release of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in monocytic cells stimulated with UDP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;330:467–473. - PubMed
-
- Crauwels HM, Van Hove CE, Holvoet P, Herman AG, Bult H. Plaque-associated endothelial dysfunction in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice on a regular diet. Effect of human apolipoprotein AI. Cardiovasc Res. 2003;59:189–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

