Longitudinal pathways linking child maltreatment, emotion regulation, peer relations, and psychopathology
- PMID: 20050965
- PMCID: PMC3397665
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2009.02202.x
Longitudinal pathways linking child maltreatment, emotion regulation, peer relations, and psychopathology
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to investigate longitudinal relations among child maltreatment, emotion regulation, peer acceptance and rejection, and psychopathology.
Methods: Data were collected on 215 maltreated and 206 nonmaltreated children (ages 6-12 years) from low-income families. Children were evaluated by camp counselors on emotion regulation and internalizing and externalizing symptomatology and were nominated by peers for peer acceptance and rejection.
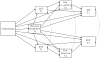
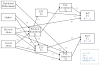
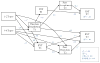
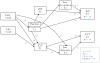
Results: Structural equation modeling analyses revealed that experiencing neglect, physical and/or sexual abuse, multiple maltreatment subtypes, and earlier onset of maltreatment were related to emotion dysregulation. Lower emotion regulation (Time 1) was associated with higher externalizing symptomatology (Time 1) that contributed to later peer rejection (Time 2), which in turn was related to higher externalizing symptomatology (Time 2). Conversely, higher emotion regulation was predictive of higher peer acceptance over time, which was related to lower internalizing symptomatology controlling for initial levels of symptomatology.
Conclusions: The findings emphasize the important role of emotion regulation as a risk or a protective mechanism in the link between earlier child maltreatment and later psychopathology through its influences on peer relations.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None
Figures
References
-
- Achenbach T. Manual for the Teacher’s Report form and 1991 Profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry; 1991.
-
- Barnett D, Manly JT, Cicchetti D. Defining child maltreatment: The interface between policy and research. In: Cicchetti D, Toth SL, editors. Child abuse, child development, and social policy. Norwood, NJ: Ablex; 1993. pp. 7–73.
-
- Bolger KE, Patterson CJ. Developmental pathways from child maltreatment to peer rejection. Child Development. 2001a;72:549–568. - PubMed
-
- Bolger KE, Patterson CJ. Pathways from child maltreatment to internalizing problems: Perceptions of control as mediators and moderators. Development and Psychopathology. 2001b;13:913–940. - PubMed
-
- Bowlby J. Attachment and loss: Vol. 1. Attachment. New York: Basic Books; 1969/1982.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

