IGF-I induced genes in stromal fibroblasts predict the clinical outcome of breast and lung cancer patients
- PMID: 20051100
- PMCID: PMC2823652
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7015-8-1
IGF-I induced genes in stromal fibroblasts predict the clinical outcome of breast and lung cancer patients
Abstract
Background: Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-I) signalling is important for cancer initiation and progression. Given the emerging evidence for the role of the stroma in these processes, we aimed to characterize the effects of IGF-I on cancer cells and stromal cells separately.
Methods: We used an ex vivo culture model and measured gene expression changes after IGF-I stimulation with cDNA microarrays. In vitro data were correlated with in vivo findings by comparing the results with published expression datasets on human cancer biopsies.
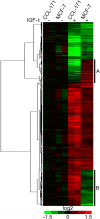
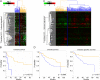
Results: Upon stimulation with IGF-I, breast cancer cells and stromal fibroblasts show some common and other distinct response patterns. Among the up-regulated genes in the stromal fibroblasts we observed a significant enrichment in proliferation associated genes. The expression of the IGF-I induced genes was coherent and it provided a basis for the segregation of the patients into two groups. Patients with tumours with highly expressed IGF-I induced genes had a significantly lower survival rate than patients whose tumours showed lower levels of IGF-I induced gene expression (P = 0.029 - Norway/Stanford and P = 7.96e-09 - NKI dataset). Furthermore, based on an IGF-I induced gene expression signature derived from primary lung fibroblasts, a separation of prognostically different lung cancers was possible (P = 0.007 - Bhattacharjee and P = 0.008 - Garber dataset).
Conclusion: Expression patterns of genes induced by IGF-I in primary breast and lung fibroblasts accurately predict outcomes in breast and lung cancer patients. Furthermore, these IGF-I induced gene signatures derived from stromal fibroblasts might be promising predictors for the response to IGF-I targeted therapies. See the related commentary by Werner and Bruchim: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1741-7015/8/2.
Figures

Comment in
-
Basic and clinical significance of IGF-I-induced signatures in cancer.BMC Med. 2010 Jan 5;8:2. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-8-2. BMC Med. 2010. PMID: 20051101 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Basic and clinical significance of IGF-I-induced signatures in cancer.BMC Med. 2010 Jan 5;8:2. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-8-2. BMC Med. 2010. PMID: 20051101 Free PMC article.
-
BMP2 response pattern in human lung fibroblasts predicts outcome in lung adenocarcinomas.BMC Med Genomics. 2015 Apr 29;8:16. doi: 10.1186/s12920-015-0090-4. BMC Med Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25924783 Free PMC article.
-
Favorable outcome associated with an IGF-1 ligand signature in breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 May;133(1):321-31. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-1952-5. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 22297468
-
A mouse mammary gland involution mRNA signature identifies biological pathways potentially associated with breast cancer metastasis.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2009 Jun;14(2):99-116. doi: 10.1007/s10911-009-9120-1. Epub 2009 Apr 30. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2009. PMID: 19408105 Review.
-
The insulin-like growth factors, their receptors, and their binding proteins in human breast cancer.Cancer Treat Res. 1991;53:93-106. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3940-7_5. Cancer Treat Res. 1991. PMID: 1672092 Review.
Cited by
-
Ordered subset analysis identifies loci influencing lung cancer risk on chromosomes 6q and 12q.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010 Dec;19(12):3157-66. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-10-0792. Epub 2010 Oct 28. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010. PMID: 21030603 Free PMC article.
-
Basic and clinical significance of IGF-I-induced signatures in cancer.BMC Med. 2010 Jan 5;8:2. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-8-2. BMC Med. 2010. PMID: 20051101 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of radioimmuno and carbon nanotube field-effect transistor assays for measuring insulin-like growth factor-1 in a preclinical model of human breast cancer.J Nanobiotechnology. 2011 Sep 2;9:36. doi: 10.1186/1477-3155-9-36. J Nanobiotechnology. 2011. PMID: 21888628 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Novel Prognostic Model for Lung Adenocarcinoma Utilizing Pyroptosis-Associated LncRNAs.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2025 Jan 13;2025:4488139. doi: 10.1155/ancp/4488139. eCollection 2025. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2025. PMID: 39834603 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal nurses' experiences with generative AI in clinical decision-making: a qualitative exploration in high-risk nicus.BMC Nurs. 2025 Apr 7;24(1):386. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-03044-6. BMC Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40197527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jones JI, Clemmons DR. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr Rev. 1995;16:3–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

