Serum levels of soluble Fas, soluble tumor necrosis factor-receptor II, interleukin-2 receptor and interleukin-8 as early predictors of hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptian patients with hepatitis C virus genotype-4
- PMID: 20051112
- PMCID: PMC2819041
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-5926-9-1
Serum levels of soluble Fas, soluble tumor necrosis factor-receptor II, interleukin-2 receptor and interleukin-8 as early predictors of hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptian patients with hepatitis C virus genotype-4
Abstract
Background: Liver disease progression from chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is associated with an imbalance between T-helper 1 and T-helper 2 cytokines. Evaluation of cytokines as possible candidate biomarkers for prediction of HCC was performed using soluble Fas(sFas), soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor-II (sTNFR-II), interleukin-2 receptor (IL-2R) and interleukin-8 (IL-8).
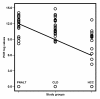
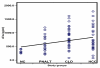
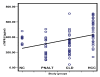
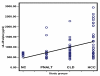
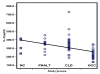
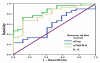
Results: The following patients were recruited: 79 with HCV infection, 30 with HCC, 32 with chronic liver disease associated with elevated liver enzyme levels (with or without cirrhosis) in addition to 17 with chronic HCV with persistent normal alanine aminotransferase levels (PNALT). Nine normal persons negative either for HCV or for hepatitis B virus were included as a control group. All persons were tested for sFas, sTNFR-II, IL-2R and IL-8 in their serum by quantitative ELISA. HCC patients had higher levels of liver enzymes but lower log-HCV titer when compared to the other groups. HCC patients had also significantly higher levels of sFas, sTNFR-II and IL-2R and significantly lower levels of IL-8 when compared to the other groups. Exclusion of HCC among patients having PNALT could be predicted with 90 % sensitivity and 70.6 % specificity when sTNFR-II is [greater than or equal to] 389 pg/ml or IL-8 is < 290 pg/ml.
Conclusions: Serum TNFR-II, IL-2Ralpha and IL-8, may be used as combined markers in HCV-infected cases for patients at high risk of developing HCC; further studies, however, are mandatory to check these findings before their application at the population level.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic Value of Serum Level of Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor IIα in Egyptian Patients With Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Hepat Mon. 2014 Sep 24;14(9):e19346. doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.19346. eCollection 2014 Sep. Hepat Mon. 2014. PMID: 25386197 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulators, sFas and Fas-L as potential noninvasive predictors of IFN treatment in patients with HCV genotype-4.J Viral Hepat. 2007 Jul;14(7):468-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2006.00832.x. J Viral Hepat. 2007. PMID: 17576388 Clinical Trial.
-
Cytokine profile in Egyptian hepatitis C virus genotype-4 in relation to liver disease progression.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Nov 14;11(42):6624-30. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i42.6624. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16425355 Free PMC article.
-
Serum biomarkers for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma associated with HCV infection in egyptian patients.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(3):1281-7. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.3.1281. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 25735368
-
Hepatitis C virus in chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma in Taiwan.Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1995;25:27-32. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1995. PMID: 8875606 Review.
Cited by
-
Early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma co-occurring with hepatitis C virus infection: A mathematical model.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Apr 28;22(16):4168-82. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i16.4168. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27122667 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Polymorphisms of Fas/FasL Promoter Associated with Hepatitis C cirrhosis and HCC.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017 Oct 26;18(10):2683-2688. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.10.2683. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017. PMID: 29072392 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble TNF-alpha-receptors I are prognostic markers in TIPS-treated patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 26;8(12):e83341. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083341. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24386183 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C virus-related lymphomagenesis in a mouse model.ISRN Hematol. 2011;2011:167501. doi: 10.5402/2011/167501. Epub 2011 Jul 26. ISRN Hematol. 2011. PMID: 22084693 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of evaluation of serum interleukin 8 levels in hepatocellular carcinoma.Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019 May;5(2):123-128. doi: 10.5114/ceh.2019.84780. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31508492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bruix J, Barrera JM, Calvet X, Ercilla G, Costa J, Sanchez-Tapias JM, Ventura M, Vall M, Bruguera M, Bru C. Prevalence of antibodies to hepatitis C virus in Spanish patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic cirrhosis. Lancet. 1989;2:1004–1006. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(89)91015-5. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
