Differential expression of Toll-like receptors on human alveolar macrophages and autologous peripheral monocytes
- PMID: 20051129
- PMCID: PMC2817655
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-11-2
Differential expression of Toll-like receptors on human alveolar macrophages and autologous peripheral monocytes
Abstract
Background: Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are critical components in the regulation of pulmonary immune responses and the recognition of respiratory pathogens such as Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (M.tb). Through examination of human alveolar macrophages this study attempts to better define the expression profiles of TLR2, TLR4 and TLR9 in the human lung compartment which are as yet still poorly defined.
Methods: Sixteen healthy subjects underwent venipuncture, and eleven subjects underwent additional bronchoalveolar lavage to obtain peripheral blood mononuclear and bronchoalveolar cells, respectively. Surface and intracellular expression of TLRs was assessed by fluorescence-activated cell sorting and qRT-PCR. Cells were stimulated with TLR-specific ligands and cytokine production assessed by ELISA and cytokine bead array.
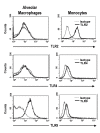
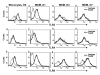
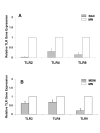
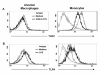
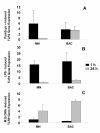
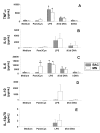
Results: Surface expression of TLR2 was significantly lower on alveolar macrophages than on blood monocytes (1.2 +/- 0.4% vs. 57 +/- 11.1%, relative mean fluorescence intensity [rMFI]: 0.9 +/- 0.1 vs. 3.2 +/- 0.1, p < 0.05). The proportion of TLR4 and TLR9-expressing cells and the rMFIs of TLR4 were comparable between alveolar macrophages and monocytes. The surface expression of TLR9 however, was higher on alveolar macrophages than on monocytes (rMFI, 218.4 +/- 187.3 vs. 4.4 +/- 1.4, p < 0.05) while the intracellular expression of the receptor and the proportion of TLR9 positive cells were similar in both cell types. TLR2, TLR4 and TLR9 mRNA expression was lower in bronchoalveolar cells than in monocytes.Pam3Cys, LPS, and M.tb DNA upregulated TLR2, TLR4 and TLR9 mRNA in both, bronchoalveolar cells and monocytes. Corresponding with the reduced surface and mRNA expression of TLR2, Pam3Cys induced lower production of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IL-6 in bronchoalveolar cells than in monocytes. Despite comparable expression of TLR4 on both cell types, LPS induced higher levels of IL-10 in monocytes than in alveolar macrophages. M.tb DNA, the ligand for TLR9, induced similar levels of cytokines in both cell types.
Conclusion: The TLR expression profile of autologous human alveolar macrophages and monocytes is not identical, therefore perhaps contributing to compartmentalized immune responses in the lungs and systemically. These dissimilarities may have important implications for the design and efficacy evaluation of vaccines with TLR-stimulating adjuvants that target the respiratory tract.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential constitutive and cytokine-modulated expression of human Toll-like receptors in primary neutrophils, monocytes, and macrophages.Int J Med Sci. 2008 Jan 4;5(1):1-8. doi: 10.7150/ijms.5.1. Int J Med Sci. 2008. PMID: 18219369 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 2 expression is decreased on alveolar macrophages in cigarette smokers and COPD patients.Respir Res. 2005 Jul 8;6(1):68. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-6-68. Respir Res. 2005. PMID: 16004610 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Innate immune responses to bacterial ligands in the peripheral human lung--role of alveolar epithelial TLR expression and signalling.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21827. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021827. Epub 2011 Jul 15. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21789185 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide transcriptional profiling of mononuclear phagocytes recruited to mouse lungs in response to alveolar challenge with the TLR2 agonist Pam3CSK4.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Oct;297(4):L608-18. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.90433.2008. Epub 2009 Jul 17. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19617307
-
TLR2 stimulation impairs anti-inflammatory activity of M2-like macrophages, generating a chimeric M1/M2 phenotype.Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 Nov 2;19(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1447-1. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29096690 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Surfactant protein-A modulates LPS-induced TLR4 localization and signaling via β-arrestin 2.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59896. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059896. Epub 2013 Mar 25. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23536892 Free PMC article.
-
Human Alveolar Macrophages Detect SARS-CoV-2 Envelope Protein Through TLR2 and TLR4 and Secrete Cytokines in Response.Immunology. 2025 Jul;175(3):391-401. doi: 10.1111/imm.13922. Epub 2025 May 4. Immunology. 2025. PMID: 40320615 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary surfactant protein A and surfactant lipids upregulate IRAK-M, a negative regulator of TLR-mediated inflammation in human macrophages.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012 Oct 1;303(7):L608-16. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00067.2012. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22886503 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell analysis reveals TLR-induced macrophage heterogeneity and quorum sensing dictate population wide anti-inflammatory feedback in response to LPS.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 24;14:1135223. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1135223. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36911668 Free PMC article.
-
Differential susceptibility to lipopolysaccharide affects the activation of toll-like-receptor 4 signaling in THP-1 cells and PMA-differentiated THP-1 cells.Innate Immun. 2022 Apr;28(3-4):122-129. doi: 10.1177/17534259221100170. Innate Immun. 2022. PMID: 35612375 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

