ANMM4CBR: a case-based reasoning method for gene expression data classification
- PMID: 20051140
- PMCID: PMC2843690
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-7188-5-14
ANMM4CBR: a case-based reasoning method for gene expression data classification
Abstract
Background: Accurate classification of microarray data is critical for successful clinical diagnosis and treatment. The "curse of dimensionality" problem and noise in the data, however, undermines the performance of many algorithms.
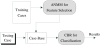
Method: In order to obtain a robust classifier, a novel Additive Nonparametric Margin Maximum for Case-Based Reasoning (ANMM4CBR) method is proposed in this article. ANMM4CBR employs a case-based reasoning (CBR) method for classification. CBR is a suitable paradigm for microarray analysis, where the rules that define the domain knowledge are difficult to obtain because usually only a small number of training samples are available. Moreover, in order to select the most informative genes, we propose to perform feature selection via additively optimizing a nonparametric margin maximum criterion, which is defined based on gene pre-selection and sample clustering. Our feature selection method is very robust to noise in the data.
Results: The effectiveness of our method is demonstrated on both simulated and real data sets. We show that the ANMM4CBR method performs better than some state-of-the-art methods such as support vector machine (SVM) and k nearest neighbor (kNN), especially when the data contains a high level of noise.
Availability: The source code is attached as an additional file of this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Recursive gene selection based on maximum margin criterion: a comparison with SVM-RFE.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Dec 25;7:543. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-543. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 17187691 Free PMC article.
-
A New Filter Approach Based on Effective Ranges for Classification of Gene Expression Data.Big Data. 2024 Aug;12(4):312-330. doi: 10.1089/big.2022.0086. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Big Data. 2024. PMID: 37668992
-
Computer-assisted lip diagnosis on Traditional Chinese Medicine using multi-class support vector machines.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2012 Aug 16;12:127. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-12-127. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2012. PMID: 22898352 Free PMC article.
-
Two-stage feature selection for classification of gene expression data based on an improved Salp Swarm Algorithm.Math Biosci Eng. 2022 Sep 19;19(12):13747-13781. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2022641. Math Biosci Eng. 2022. PMID: 36654066
-
Effects of Distance Measure Choice on K-Nearest Neighbor Classifier Performance: A Review.Big Data. 2019 Dec;7(4):221-248. doi: 10.1089/big.2018.0175. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Big Data. 2019. PMID: 31411491 Review.
Cited by
-
MIDClass: microarray data classification by association rules and gene expression intervals.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 6;8(8):e69873. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069873. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23936357 Free PMC article.
-
An enhancement of binary particle swarm optimization for gene selection in classifying cancer classes.Algorithms Mol Biol. 2013 Apr 24;8(1):15. doi: 10.1186/1748-7188-8-15. Algorithms Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23617960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Golub TR, Slonim DK, Tamayo P, Huard C, Gaasenbeek M, Mesirov JP, Coller H, Loh ML, Downing JR, Caligiuri MA, Bloomfield CD, Lander ES. Molecular classification of cancer: class discovery and class prediction by gene expression monitoring. Science. 1999;286:531–537. doi: 10.1126/science.286.5439.531. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khan J, Wei JS, Ringnér M, Saal LH, Ladanyi M, Westermann F, Berthold F, Schwab M, Antonescu CR, Peterson C, Meltzer PS. Classification and diagnostic prediction of cancers using gene expression profiling and artificial neural networks. Nat Med. 2001;7:673–679. doi: 10.1038/89044. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

