Characterization of BNT2, an intrinsically curved DNA of Escherichia coli O157:H7
- PMID: 20051226
- PMCID: PMC2814767
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.12.160
Characterization of BNT2, an intrinsically curved DNA of Escherichia coli O157:H7
Abstract
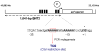
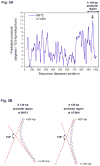
The gene regulation by intrinsically curved DNA is one way for bacterial sensing of and response to environmental changes. Previously, we showed that the genetic element BNT2 upstream of the ecf (eae-positive conserved fragment) operon in the Escherichia coli O157:H7 virulence plasmid (pO157) has characteristics typical of intrinsically curved DNA, including the presence of multi-homopolymeric adenine:thymine tracts (AT tracts) and electrophoretic anomaly at 4 degrees C. Here we report that a local intrinsic curvature induced by the two phased AT tracts within the unusual promoter sequence of BNT2 played a major role for its temperature-dependent promoter activity. The base substitution of the AT tract in the spacer DNA between the -35 and the unusual -10 regions of the BNT2 promoter with non-AT tract sequence reduced intrinsic curvature slightly at 4 degrees C, but greatly affected its transcriptional activity. This implies that such a local intrinsic curvature within the unusual promoter of BNT2 is important for thermoregulation of the ecf operon.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- de Jonge R, Takumi K, Ritmeester WS, van Leusden FM. The adaptive response of Escherichia coli O157 in an environment with changing pH. J Appl Microbiol. 2003;94:555–60. - PubMed
-
- Naylor SW, Roe AJ, Nart P, Spears K, Smith DG, Low JC, Gally DL. Escherichia coli O157 : H7 forms attaching and effacing lesions at the terminal rectum of cattle and colonization requires the LEE4 operon. Microbiology. 2005;151:2773–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

